Power Transmission And Distribution
Power Transmission & Distribution (T&D) Safety: Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) with Safety Padlocks
1. Critical Safety Risks in T&D Systems
- Electrocution: Contact with live circuits (480V+ in distribution, 110kV+ in transmission).
- Arc Flash/Blast: Explosive energy release from accidental energization (can reach temperatures of 35,000°F).
- Mechanical Hazards: Unintended movement of switchgear, circuit breakers, or rotating parts (e.g., pump motors).
- Thermal Burns: From energized equipment overheating or failed isolation.
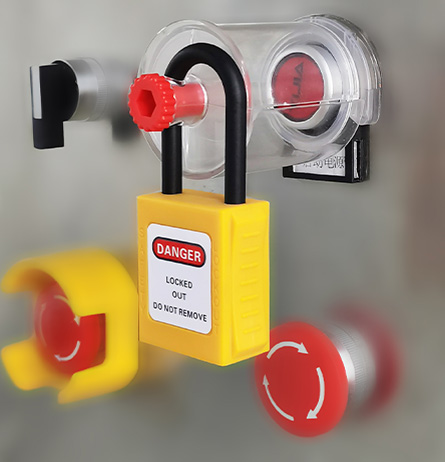
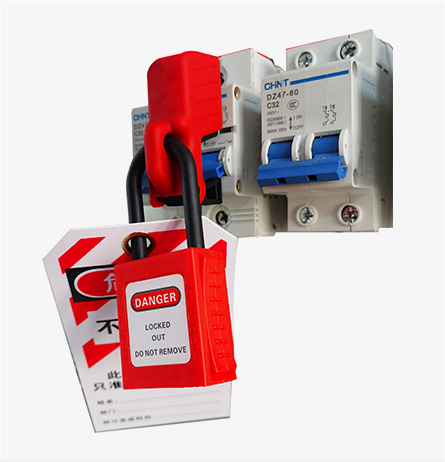
A. Energy Isolation Points & Padlock Applications
T&D Equipment Energy Source Isolation Device Safety Padlock/Accessory Example Use Case Substation Circuit Breakers Electrical (110kV–500kV) Breaker switches, disconnects Heavy-duty stainless steel padlocks with breaker lockout kits Locking a 230kV breaker during transformer maintenance Distribution Panel Switches Low-voltage (120V–600V) Toggle switches, fuse boxes Insulated nylon padlocks (UL 94 V-0 rated) Securing a 480V panel during meter replacement Transformer Disconnects Electrical/Inductive Disconnect switches, grounding pads Weatherproof padlocks (IP67) with anti-vibration shackles Locking a 10MVA transformer’s primary disconnect Generator Circuit Breakers Mechanical/Electrical Breaker interlocks, control panels Keyed-alike padlocks for multi-point isolation (e.g., 3-phase systems) Preventing accidental startup of a standby generator Underground Cable Junctions Electrical (HV/LV) Cable disconnectors, test points Corrosion-resistant padlocks (316 stainless steel) Isolating a 33kV underground feeder during fault repair

Core Elements of a Lockout Solution
-
Circuit breakers lockout
>Padlocks
Circuit breakers (HV/MV/LV), disconnect switches, fuse panels, and relay controls.
Valve Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Plug and Electrical Lockouts
Pneumatic and Hydraulic Lockouts
Cable Lockouts
-
Safety Padlock
>Padlocks
Safety padlocks physically secure energy-isolating devices (e.g., circuit breakers, valves) during maintenance to prevent accidental energization, aligning with Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures .
Valve Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Plug and Electrical Lockouts
Pneumatic and Hydraulic Lockouts
Cable Lockouts
-
Lockout Kits
>Padlocks
Used to lock specific energy control points, preventing accidental reactivation. They are often color-coded and can be keyed differently or keyed alike.
Valve Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Plug and Electrical Lockouts
Pneumatic and Hydraulic Lockouts
Cable Lockouts
-
Hasps
>Padlocks
Used to lock specific energy control points, preventing accidental reactivation. They are often color-coded and can be keyed differently or keyed alike.
Valve Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Plug and Electrical Lockouts
Pneumatic and Hydraulic Lockouts
Cable Lockouts
-
Group Lock Boxes
>Padlocks
Used to lock specific energy control points, preventing accidental reactivation. They are often color-coded and can be keyed differently or keyed alike.
Valve Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockouts
Plug and Electrical Lockouts
Pneumatic and Hydraulic Lockouts
Cable Lockouts
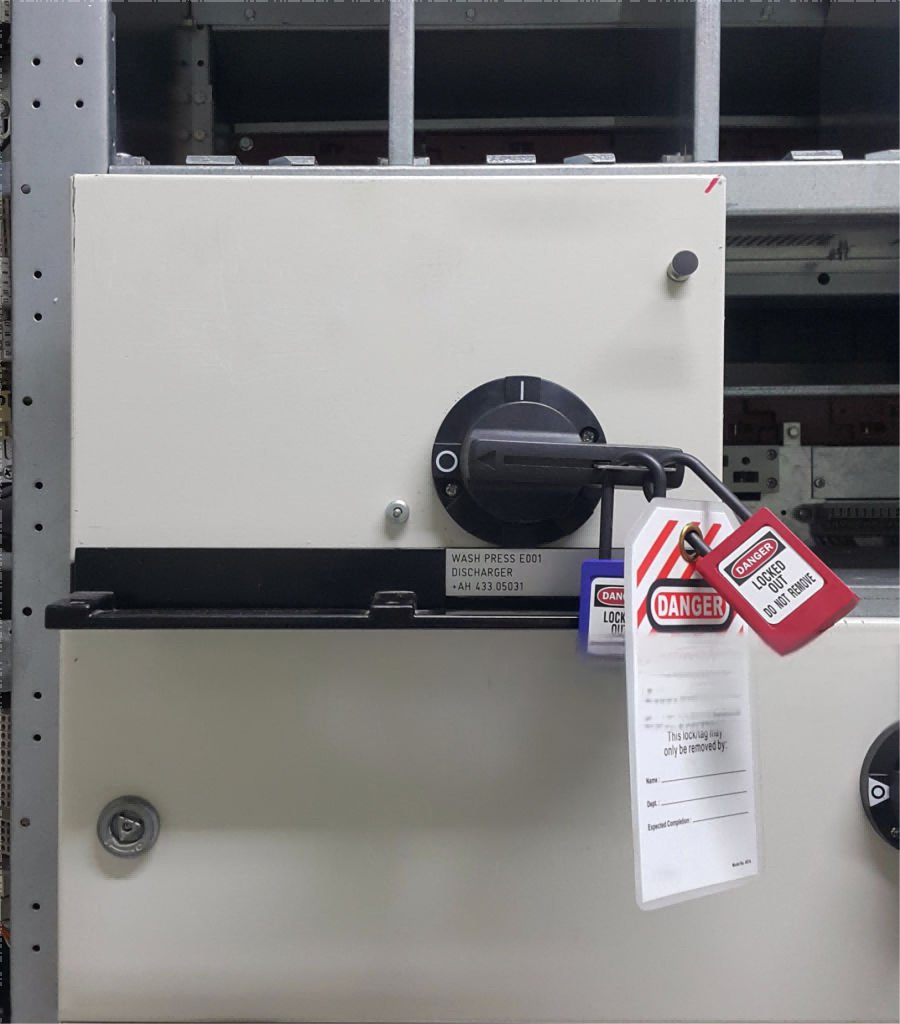
Steps for Implementing a Lockout Solution (LOTO Procedure)
-

Preparation
Identify all energy sources connected to the machinery or system that requires servicing.
-

Shutdown
Power down the equipment following the proper shutdown procedure for the specific machine or system.
-

Isolation
Physically isolate the machine or equipment from all its energy sources (electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, etc.) using the appropriate lockout devices (e.g., padlocks, valve lockouts).
-

Lockout
Apply lockout devices to all energy-isolating points. Each worker involved in the maintenance should apply their own lock, ensuring multiple levels of protection.
-

Tagout
Attach tags to all locked-out devices, providing clear information about who is responsible for the lockout and the purpose.
-

Release Stored Energy
Safely release any stored energy (e.g., hydraulic pressure, residual electrical energy) in the system to prevent accidental activation.
-

Verification
Verify that the lockout was successful by attempting to operate the machine’s controls to ensure it cannot be energized.
-

Maintenance/Servicing
Perform the required maintenance or servicing while ensuring the lockout remains in place.
-

Re-energizing the Equipment
After the work is completed, verify that all tools and workers are clear from the area. Remove locks in reverse order, with each worker removing their lock only when their part of the work is complete.
-

Restart
Restore energy to the equipment and test it to ensure proper functionality.
CUSTOMER CASES

Rongxian Power Supply Company: Cost-Effective Mechanical Locks
Challenge:
Residential distribution boxes in rural areas faced frequent unauthorized access.
Solution:
316 Stainless Steel Padlocks:
Corrosion-resistant for coastal environments .
Warning labels with emergency contact information.
Community Engagement:
Door-to-door education on lockout safety.
Results:
Zero 触电 incidents since 2018.
Resident complaints reduced by 90%.
Awarded "Sichuan Province Power Safety Model Project."

State Grid Zhuhai
Challenge:
2,000+ high-voltage assets required real-time tracking to prevent theft and misoperation.
Solution:
RFID-Enabled Locks:
Each lock linked to a unique asset ID via handheld scanners .
Tamper-proof design triggers alerts if forcibly removed.
GIS Integration:
Real-time asset location mapping for efficient resource allocation.
Results:
100% asset recovery rate for lost equipment.
30% reduction in manual 巡检 time.
National Grid "Digital Transformation Excellence" award.
CUSTOMER REVIEWS
What travelers community are saying.

A***e
⭐ ⭐ ⭐ ⭐ ⭐
I really enjoyed interacting with the supplier. Everything went smoothly and professionally. The products were dispatched and received on time and the quality is impeccable. I would recommend this supplier as they are truly professional and friendly. I didn't experience any problem and I appreciate this smooth transaction.

U***e
⭐ ⭐ ⭐ ⭐ ⭐
Good Quality products. I will order from them again. Good customer service.

J***o
⭐ ⭐ ⭐ ⭐ ⭐
The products they make are of great quality, the customer service is excellent, and everyone is very professional.

K***y
⭐ ⭐ ⭐ ⭐ ⭐
conforme à ma description. je suis très satisfait et recommande vos produits et services

Lockout Solution FAQ
-
What are the primary safety challenges in T&D?
-Arc Flash: High-energy explosions (NFPA 70E defines flash protection boundaries) .
Electrical Shock: Direct contact with energized components .
Equipment Failure: Faults in transformers or switches leading to unplanned outages .
Hazardous Energy Control: Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) compliance to prevent accidental energization . -
How does T&D comply with safety standards?
+OSHA 1910.269: Specifies LOTO requirements for power generation, transmission, and distribution, including energy isolation and worker training .
IEC 62271-200: Mandates safety interlocks for medium-voltage (MV) switchgear to prevent unauthorized access .
NFPA 70E: Requires arc flash hazard analysis and personal protective equipment (PPE) . -
What types of safety padlocks are used in T&D?
+Mechanical Padlocks:
316 Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant for coastal environments .
Nylon: Non-conductive for electrical applications (ASTM F1506 compliant) .
Electronic Padlocks:
Bluetooth/NB-IoT: Real-time status monitoring (e.g., Vanma WM-2000C-L35) .
GPS-Enabled: Track asset location and unauthorized access (e.g., GAO Tek GPS Padlock) .
IoT-Enabled Locks: Integrate with SCADA systems for geofencing and remote access . -
How to select the right safety padlock?
+Voltage Rating: HV (≥1kV) vs. LV (<1kV) compatibility.
Environmental Resistance: IP68 waterproofing for underwater use; UV resistance for outdoor settings .
Shackle Strength: Tensile resistance ≥2,000 lbs for industrial applications .
Standards Compliance: OSHA 1910.147, IEC 60204-1, and ASTM F1506 . -
What are the latest trends in lockout solutions?
+IoT & AI Integration:
Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes sensor data to predict lockout needs (e.g., vibration analysis for transformers) .
Real-Time Monitoring: 5G-connected locks (e.g., Digital Keys’ Wanlock) send instant alerts for unauthorized access .
Blockchain: Tamper-proof records secure lockout data (e.g., energy transactions) .
VR Training: Simulate LOTO procedures for high-risk tasks (e.g., substation maintenance) . -
How do smart grids enhance lockout safety?
+IoT-Enabled Locks: Real-time status updates on grid maps (e.g., Enedis’ IBM Watson IoT Platform) .
Fault Location Systems: FLISR (Fault Location, Isolation, and Restoration) automatically isolates faults and updates lockout zones .
5G Connectivity: Instant alerts for unauthorized access or equipment failure . -
What are the OSHA requirements for LOTO in T&D?
+1910.147: Requires written LOTO procedures, employee training, and periodic inspections .
1910.269: Specifies additional controls for power generation and transmission, including energy isolation and worker notification . -
How to maintain lockout devices?
+Lubrication: Use PTFE-based lubricants (e.g., Master Lock 2300D) to prevent corrosion .
Weatherproofing: UV-resistant coatings for coastal areas; IP68-rated locks for underwater use .
Compliance Audits: Regularly inspect locks for wear and test shackle strength . -
What are the consequences of non-compliance?
+Fines: OSHA penalties for LOTO violations range from $13,653 to $136,532 per violation .
Safety Risks: Non-compliance increases the risk of arc flashes, electrocution, and equipment damage . -
How to handle emergency lockout removal?
+Authorized Personnel Only: Supervisors or trained personnel may remove locks in emergencies .
Documentation: Record the reason for removal and notify affected workers .
Re-Lockout: Re-apply locks after the emergency to prevent re-energization .