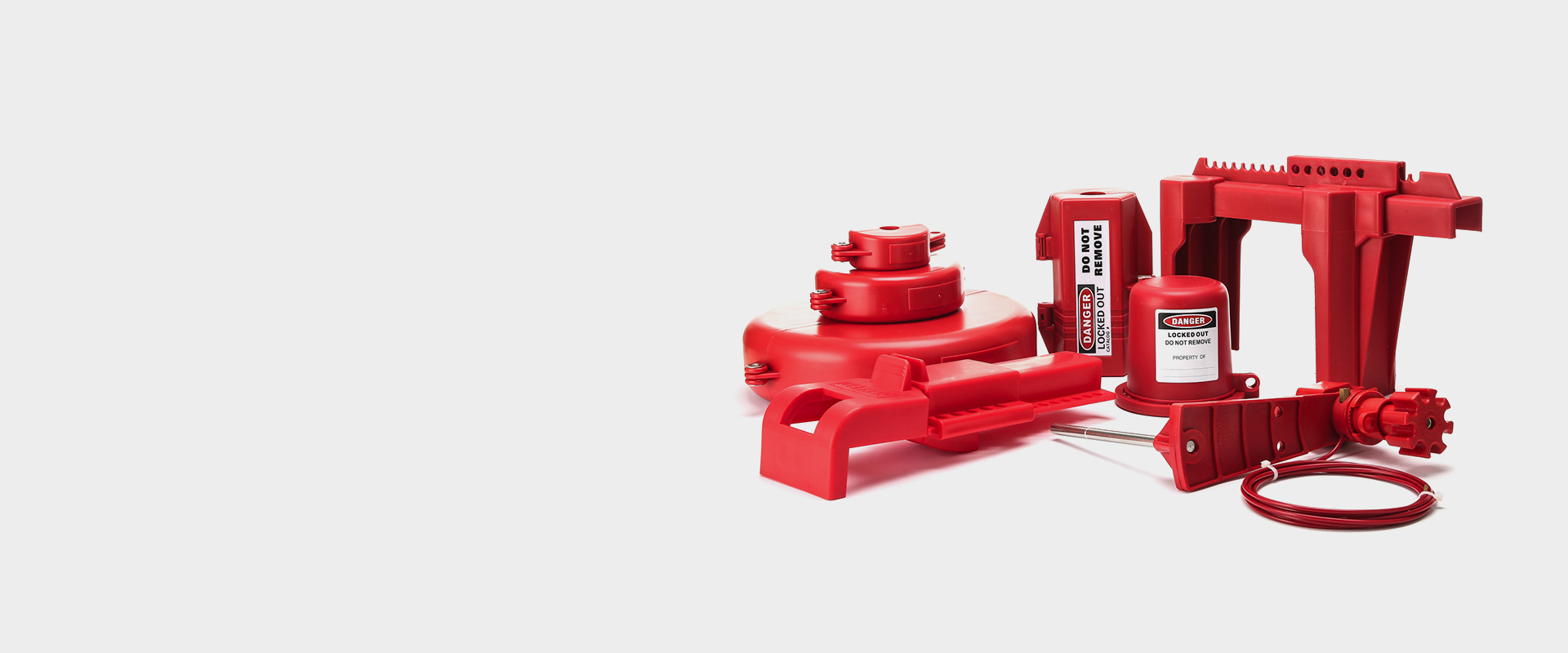
Valve Lockouts
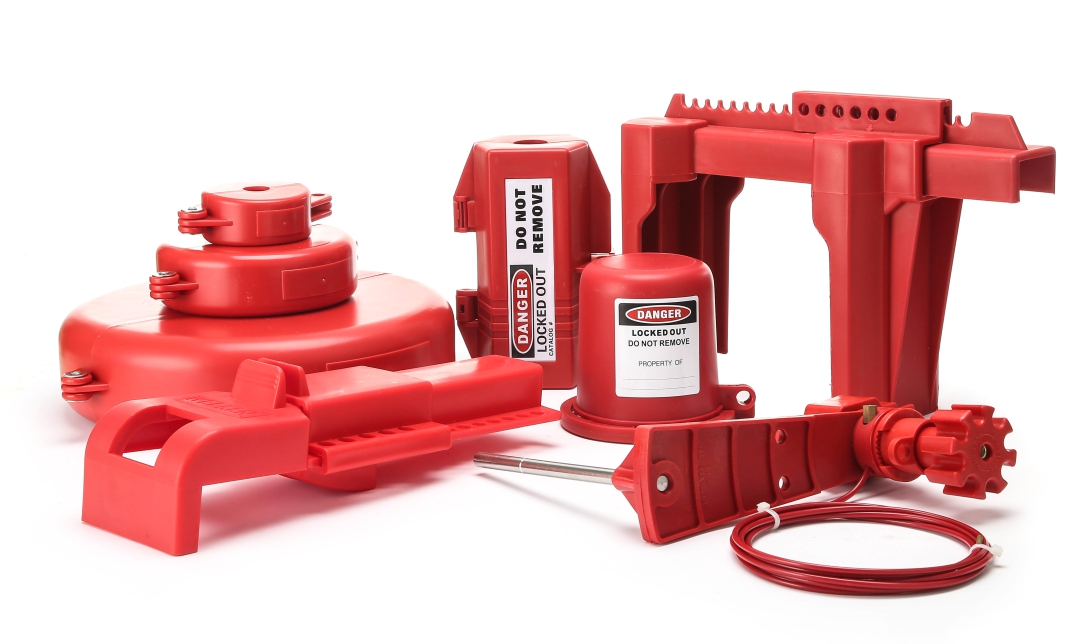
Valve Lockouts The core defense line for ensuring industrial safety Valve lockouts are indispensable safety tools in industrial equipment maintenance. Through physical locking, they prevent accidental release of energy and ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. We provide a full range of valve locking solutions, covering various types such as ball valves, gate valves, and butterfly valves, meeting the stringent needs of industries such as petrochemical, power generation, and water treatment. Product types and functions Ball valve locking device Universal ball valve lock: Suitable for ball valves from 0.5" to 4", made of high-strength nylon or stainless steel, and can withstand extreme temperatures from -40°C to 120°C. T-handle ball valve lock: With a quick locking design, it supports handle diameters from 33mm to 46mm. The net weight is only 142 grams, facilitating one-handed operation. Four-legged ball valve lock: With a patented four-legged structure, it is suitable for ball valves from 1" to 2.5". The anti-vibration performance is increased by 30% to prevent accidental loosening.
-
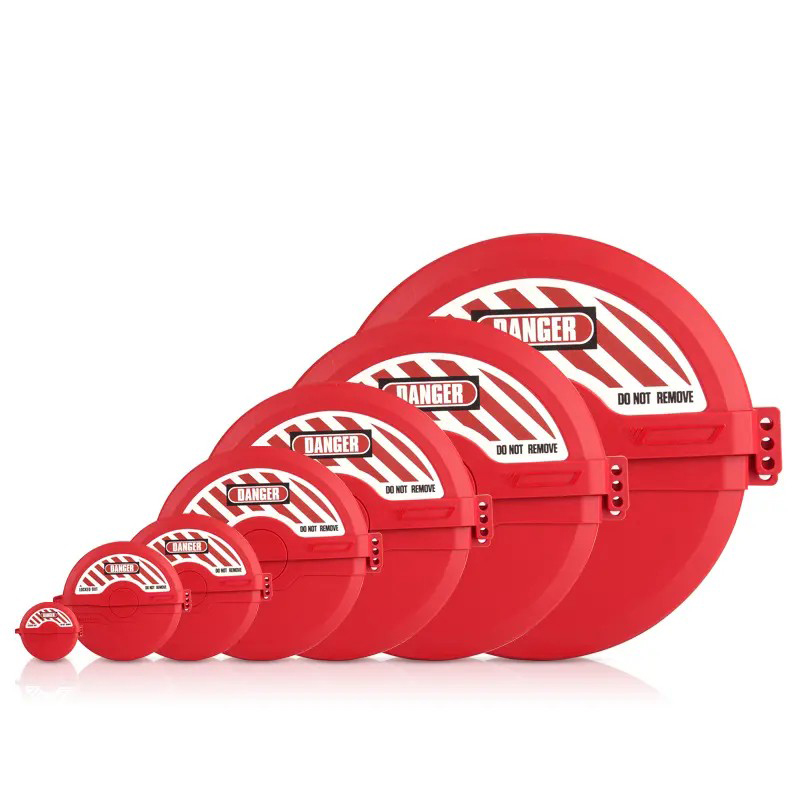
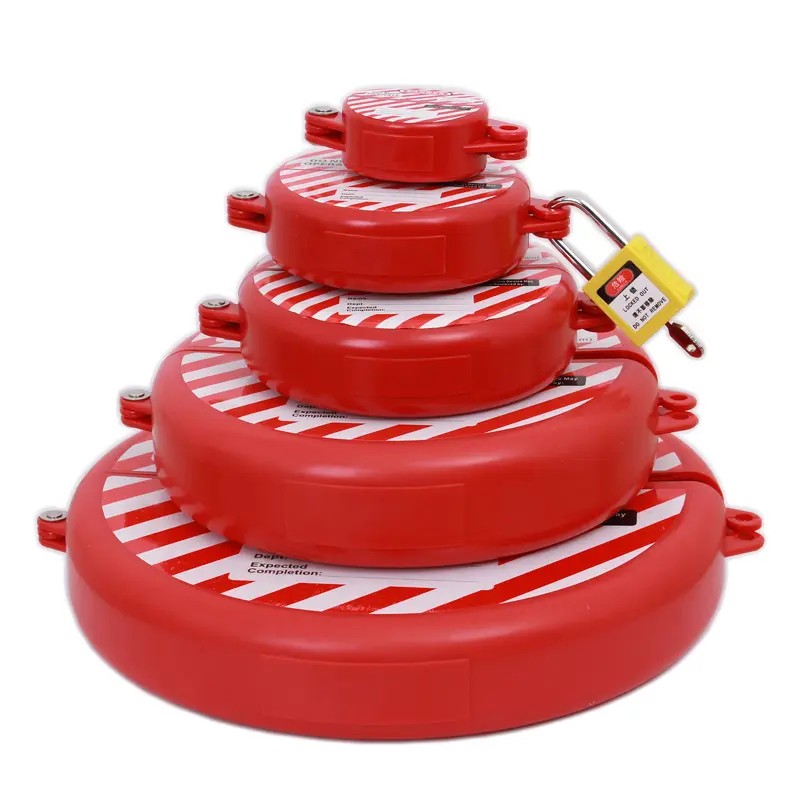
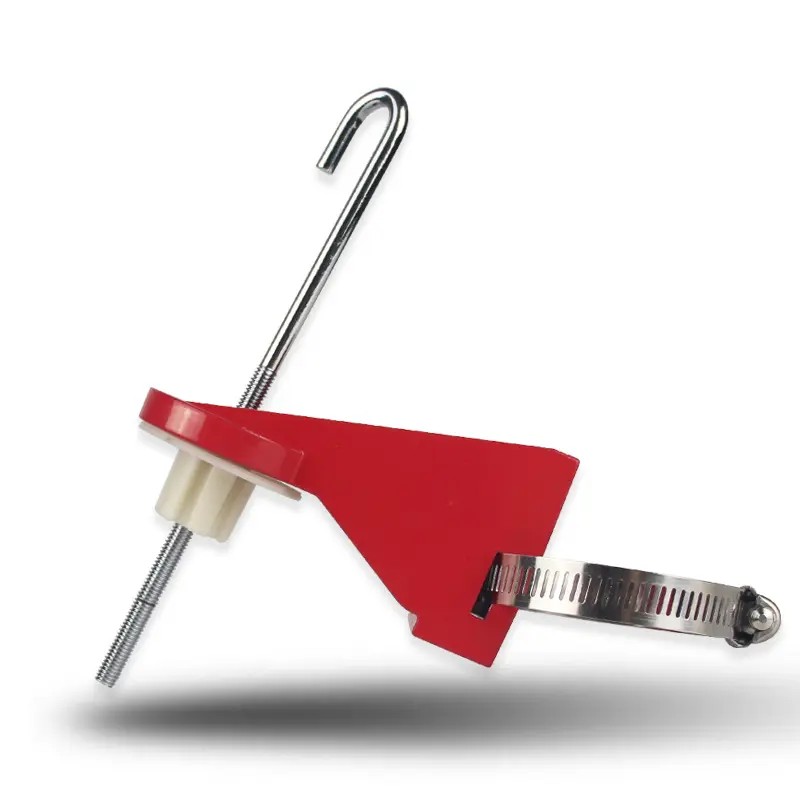
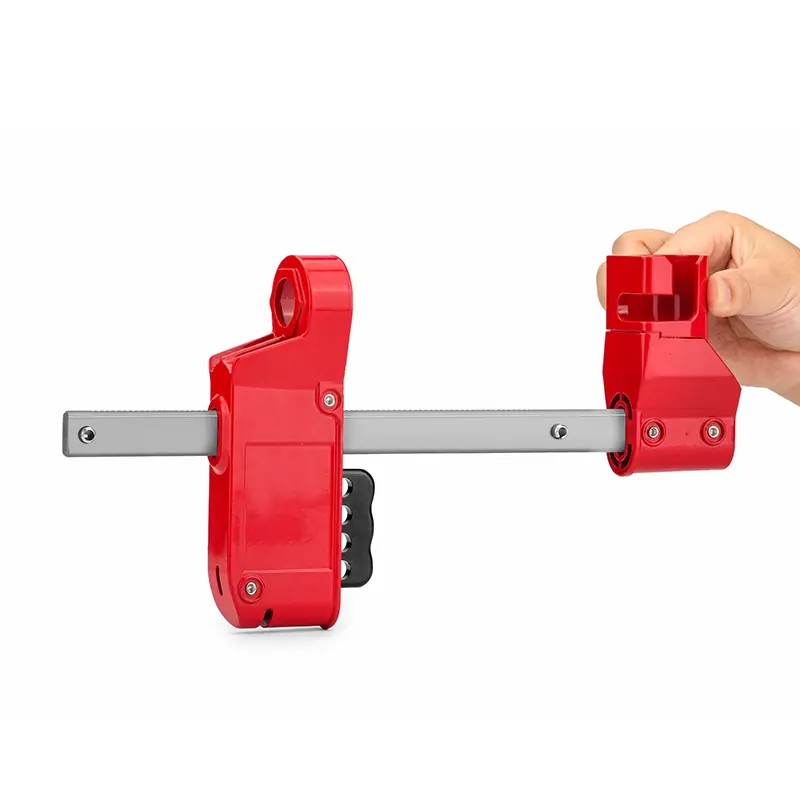
EP-F08 Polypropylene PP valve lockouts for flange ball valve
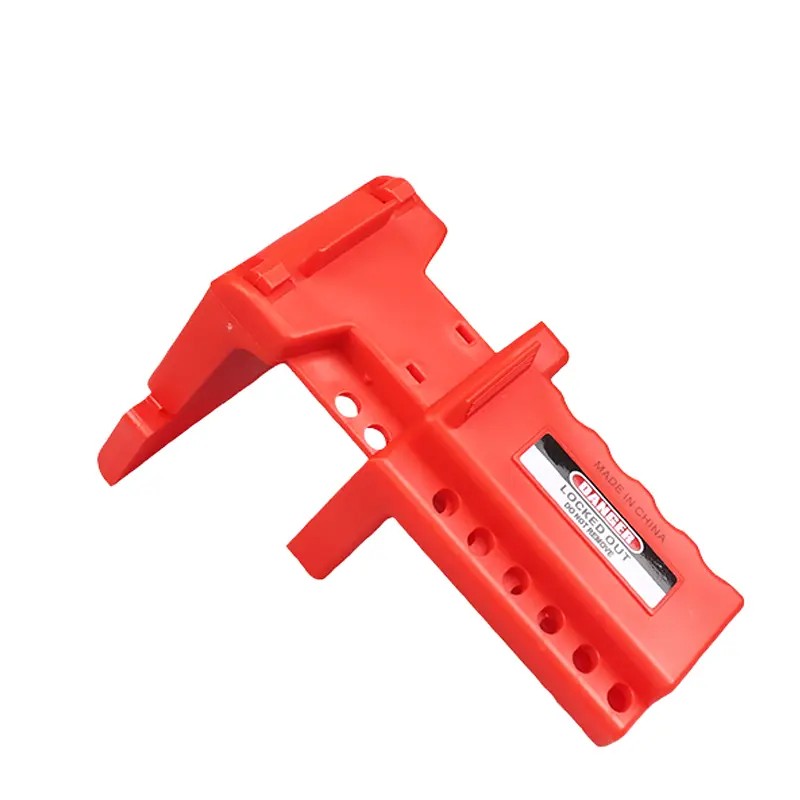
ADJUSTABLE FLANGE VALVE LOCKOUT
Inquiry -
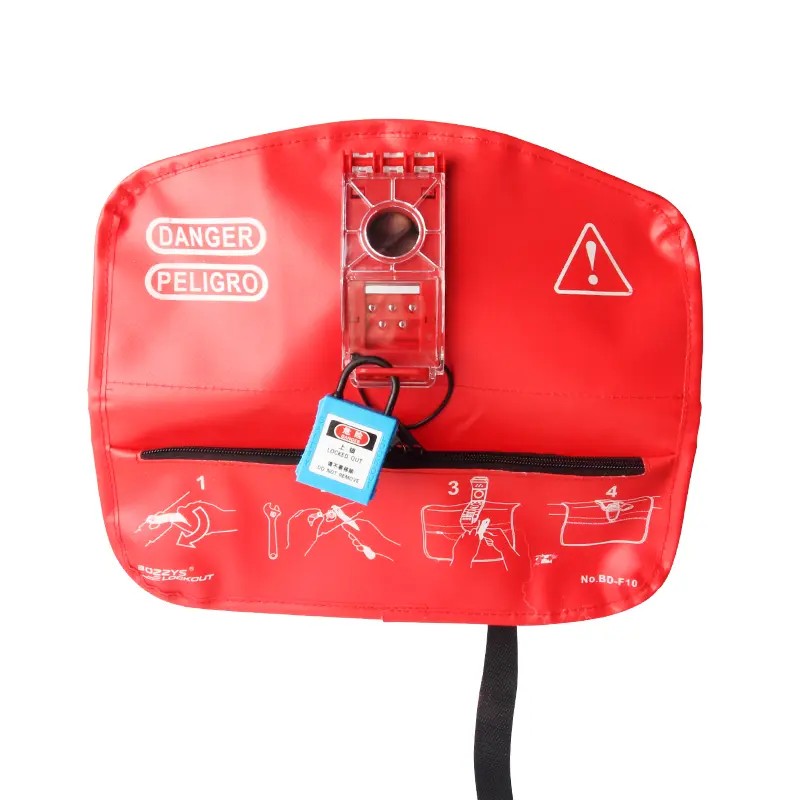
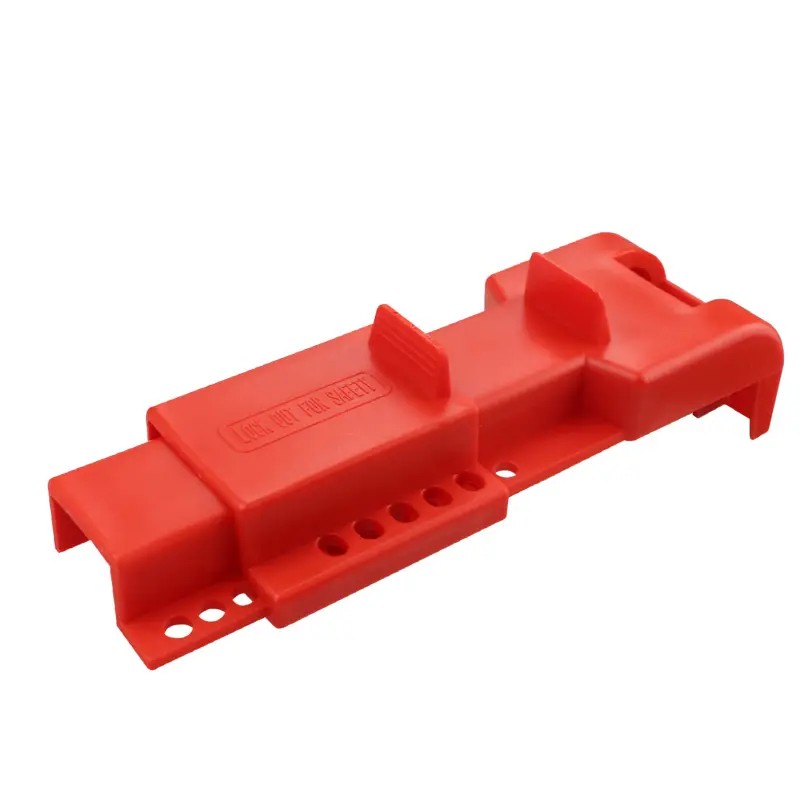
EP-F10 Wear-resistant bag valve lockouts with handle storage pocket
Adjustable Flanged Ball Valve Lockout bag
Inquiry
PRODUCT ADVANTAGES
-
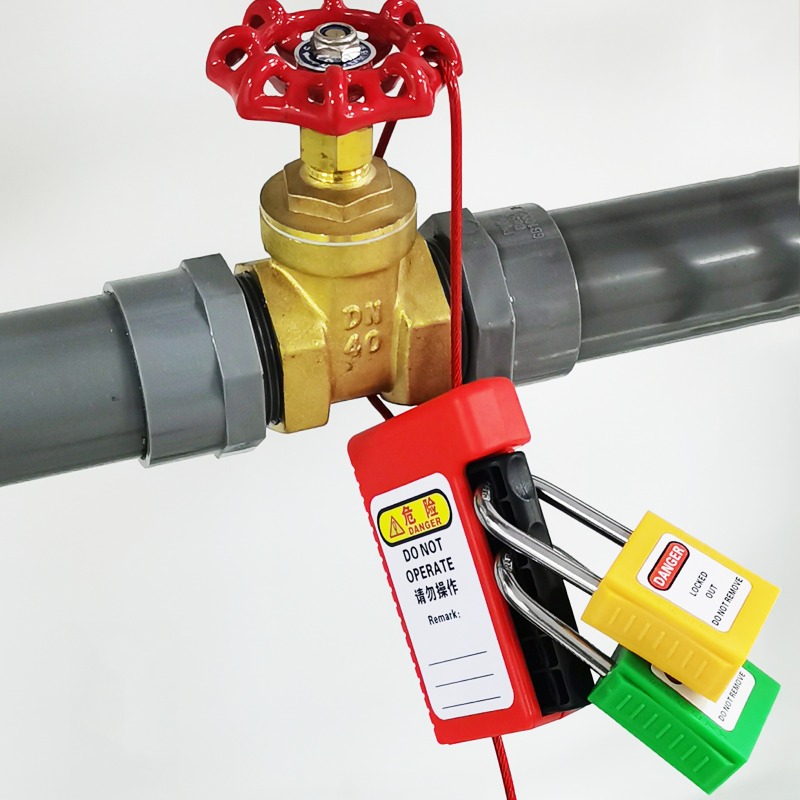

Perforated cable lock
Product model: EP- C15
Description: Lock single or multiple adjacent switches. After the key is pulled out, the steel cable can still be tightened infinitely, and multiple people can be locked at the same time. -
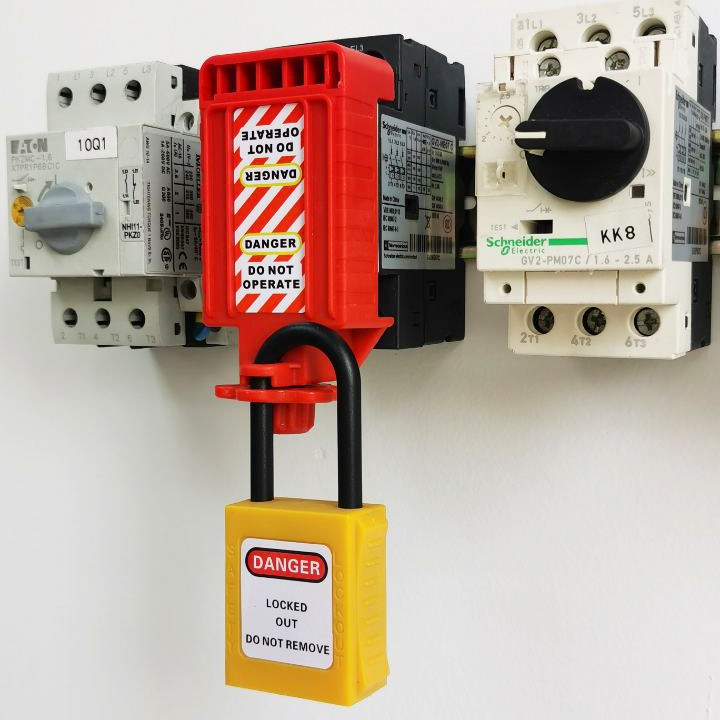

Circuit breaker lock
Model: EP-E26
Description: Mainly used for locking motor/motor circuit breaker switches
Features:
1. Made of reinforced nylon, strong and durable
2. Metal tooth clamping design, more stable locking
3. Loosen/tighten by hand, fast locking
4. Locking length: 41-57mm, width 38mm, height 22mm -

Button switch lock
Product model: EP-E39
Description: It can lock button switches with labels and various button switches at close range -
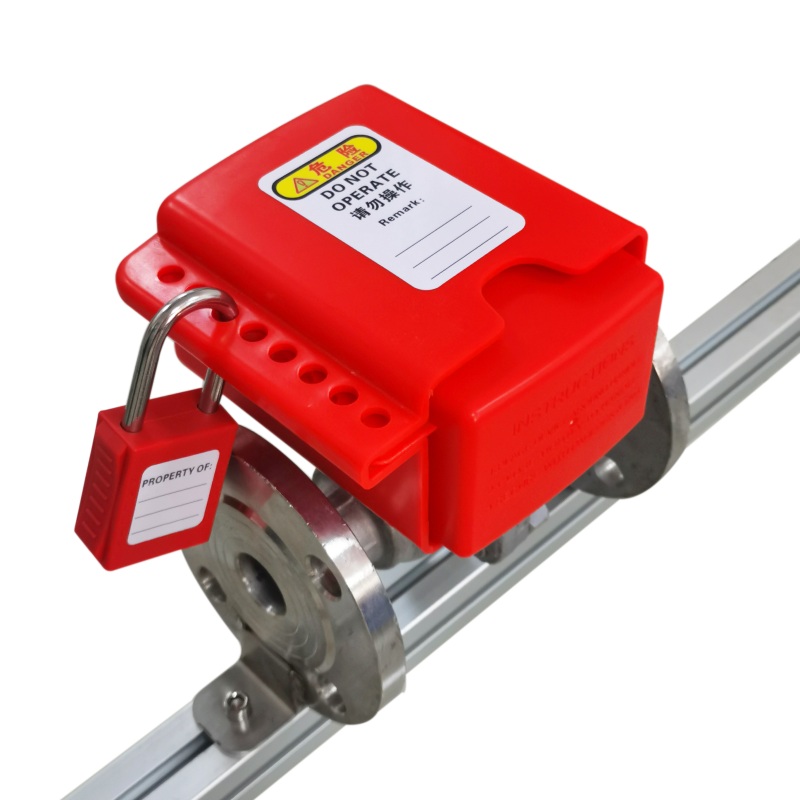

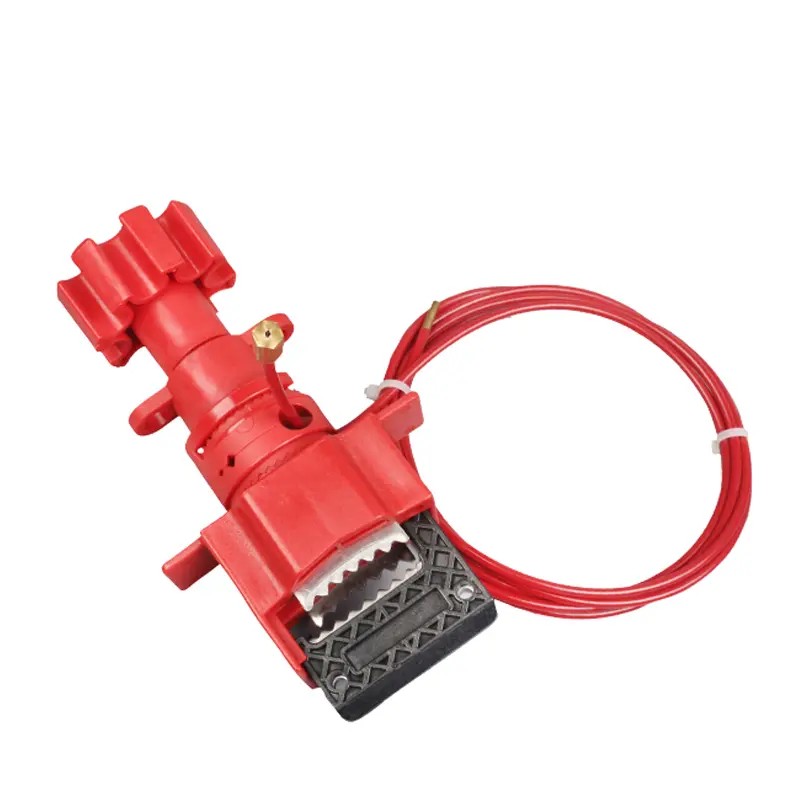
Plug valve lock
Model: EP-V42
Description: Mainly used for locking flanged ball valves/plug valves
Features:
1. Made of engineering plastics, light and tough
2. Simple structure and easy operation
3.8 hole design is easier to adjust and lock
4. Locking range: <DN150 -
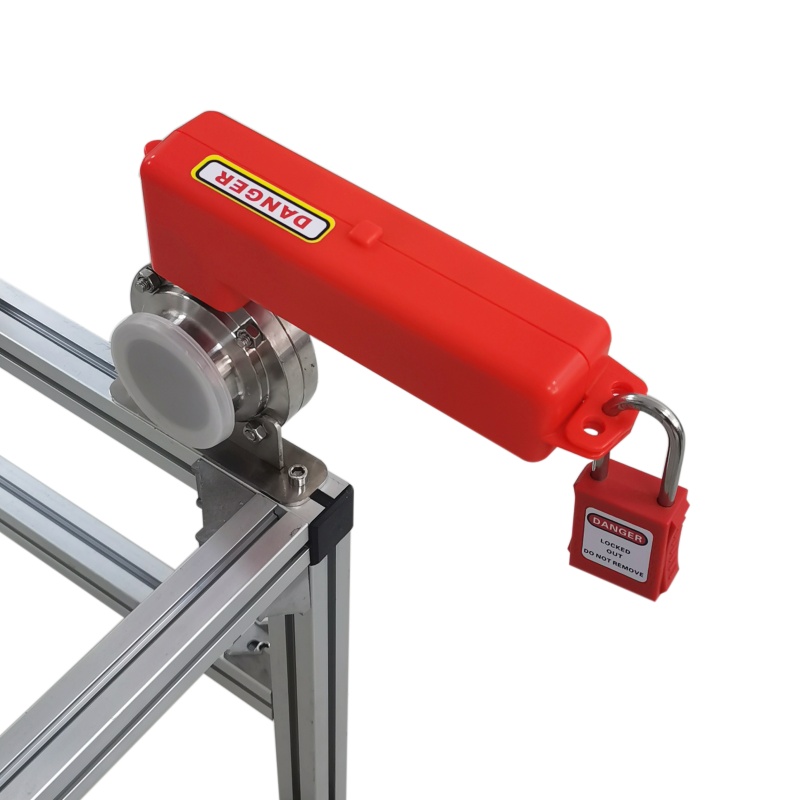

Sanitary butterfly valve lock
Model: EP-V24
Description: Mainly used for locking sanitary butterfly valves
Features:
1. Made of engineering plastics, strong and durable
2. Patented package structure design, easy to lock and easy to operate
3. It can lock most of the existing sanitary butterfly valves
4. With 2 diameter 8mm and 1 diameter 6.5mm upper lock holes -
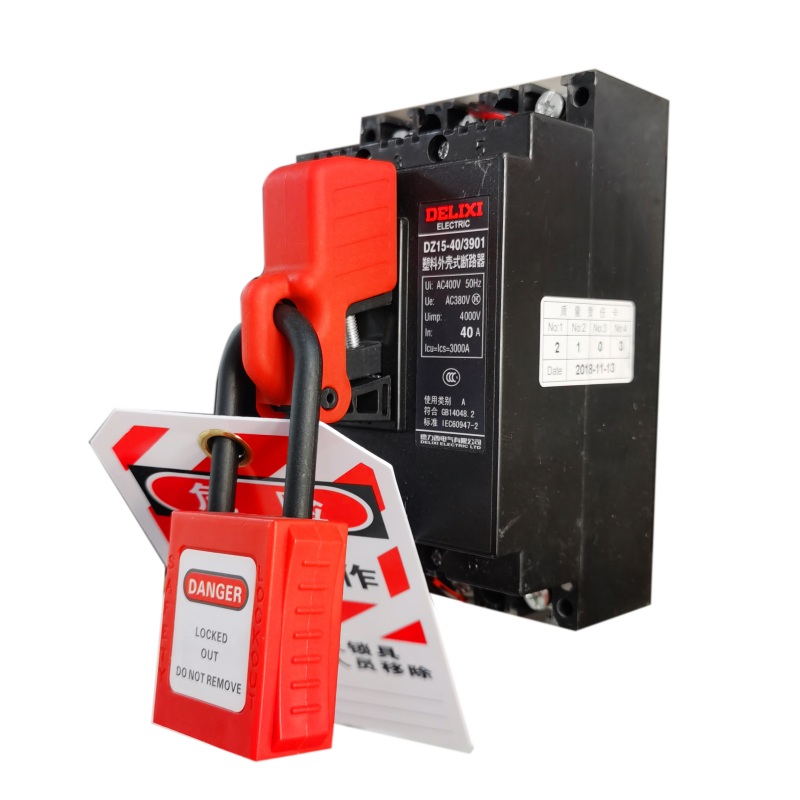

Multifunctional circuit breaker lock
Name: multifunctional circuit breaker lock
Model: EP-E15A
Description: It can not only lock the miniature molded case circuit breaker switch but also lock the miniature circuit breaker switch. -
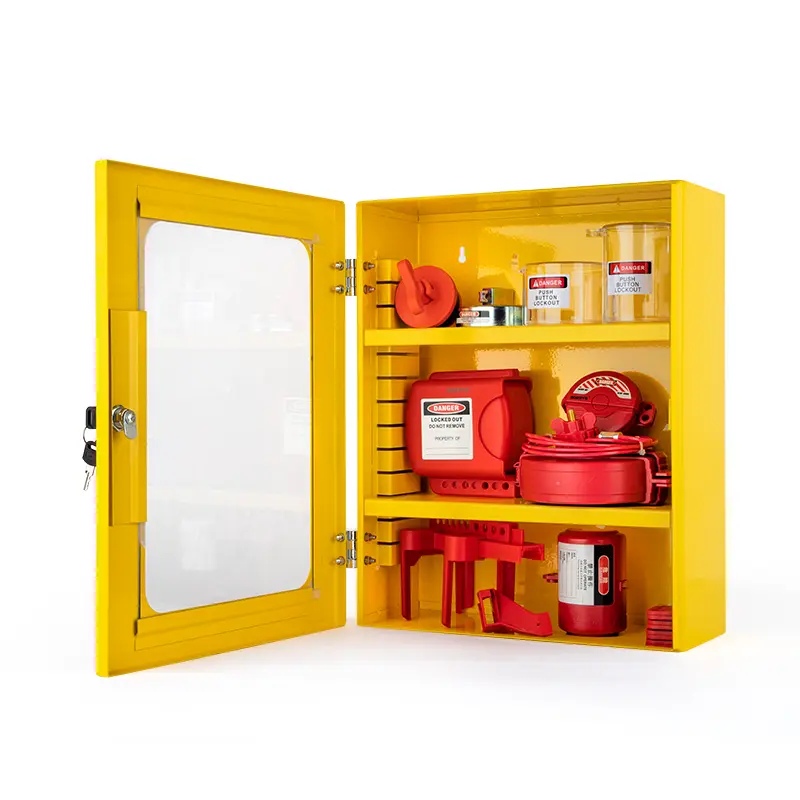

Lockout tagout stations
Model No.: EP-X07
The Lockout tagout stations size:width × height × thickness: 360mm × 450mm × 155mm,With two mobile division plates, can set the division space flexibly. -
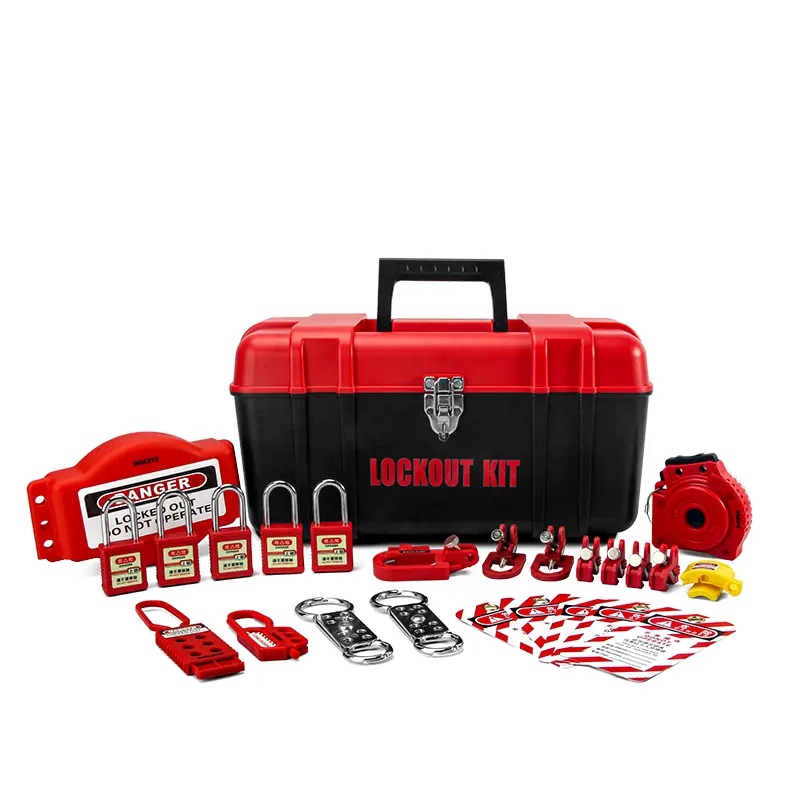

Lockout tagout kits
Lockout Tagout Kits includes:
Safety padlock *1 set
1 set of lockout box
1 set of miniature circuit breaker lockout
1 set of clamp breaker lockout
1 set of 6 holes lockout hasp
1 pcs Aluminum lockout hasp,plug lockout
1 set of emergency stop lockout
Safety Tag
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
-
What Are Valve Lockouts and Why Are They Essential?
-Valve lockouts are safety devices designed to prevent the unauthorized operation of valves during maintenance, repair, or other hazardous work. These devices physically secure valves in either the open or closed position, ensuring that they cannot be accidentally adjusted, which could lead to leaks, spills, or the release of hazardous substances. Valve lockouts are crucial for compliance with safety regulations such as OSHA (29 CFR 1910.147) and ANSI/ISA-84.00.07, safeguarding workers from potential exposure to dangerous chemicals, high-pressure fluids, or gases. By maintaining valves in a controlled state, lockouts play a vital role in preventing industrial accidents and protecting both personnel and the environment.
-
What Are the Primary Safety Standards Governing Valve Lockouts?
+The key regulatory standards for valve lockouts include:
1:OSHA Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Standard (1910.147): Mandates the control of hazardous energy sources during equipment servicing, requiring written procedures, proper training, and regular inspections. This standard applies to all types of valves, ensuring that they are effectively isolated from potential energy sources.
2:ANSI/ISA-84.00.07: Focuses on the management of process safety in industrial automation systems, including guidelines for valve isolation and lockout procedures to prevent unexpected process changes.
3:API Standards: Such as API 622 and API 624, which provide requirements for valve emissions control and testing, often involving the use of lockouts to ensure valves remain in a safe state during related operations. Compliance with these standards is not only a legal requirement but also essential for maintaining a high level of safety and operational integrity. -
How Do You Implement a Valve Lockout Procedure Correctly?
+Follow these steps for an effective valve lockout procedure:
1:Plan Ahead: Identify the type of valve (ball valve, gate valve, butterfly valve, etc.) and the associated hazards. Determine the appropriate lockout device based on the valve’s size, design, and operating pressure.
2:Notify Personnel: Inform all relevant workers about the upcoming lockout, including the location of the valve, the work to be performed, and the expected duration.
3:Isolate the Valve: Close or open the valve as required by the maintenance task, ensuring that the process is safely shut down or redirected.
4:Apply the Lockout Device: Secure the valve in position using a suitable lockout device, such as a ball valve lockout, gate valve lockout, or universal valve lock. Make sure the lock is properly attached and the key is retained by the authorized worker.
5:Verify the Lockout: Check that the valve cannot be operated by attempting to move it gently. Use appropriate monitoring tools, if necessary, to confirm that there is no flow or pressure change.
6:Tag the Valve: Attach a lockout tag with clear instructions, such as “Do Not Operate,” and include the name of the person who applied the lockout and the date.
7:Release the Lockout: Only remove the lockout device and tag after the work is completed, all safety checks are passed, and all personnel are accounted for. -
What Types of Valve Lockout Devices Are Available?
+There is a wide range of valve lockout devices to suit different valve types:
1:Ball Valve Lockouts: Specifically designed for ball valves, these lockouts secure the handle in either the open or closed position, preventing accidental rotation. They come in various sizes to fit different valve diameters.
2:Gate Valve Lockouts: Ideal for gate valves, these devices lock the valve stem or wheel, ensuring that the valve remains in the desired state. Some models are adjustable to accommodate different valve sizes.
3:Butterfly Valve Lockouts: These lockouts fit over the handle or actuator of butterfly valves, immobilizing the valve to prevent unauthorized operation.
4:Universal Valve Lockouts: Versatile devices that can be used on multiple valve types. They are adjustable and can be adapted to different valve sizes and configurations, making them a cost-effective solution for facilities with diverse valve systems.
5:Pinch Valve Lockouts: Designed for pinch valves, these lockouts hold the valve in a closed position, preventing any flow through the valve. -
How Often Should Valve Lockout Devices Be Inspected and Maintained?
+Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial for the reliability of valve lockout devices:
1:Daily Checks: Visually inspect lockout devices before each use for any signs of damage, such as cracks, deformation, or loose parts. Check that the locking mechanism operates smoothly.
2:Monthly Inspections: Conduct a more detailed inspection, including testing the strength of the lock and the integrity of the materials. Replace any components that show signs of wear or corrosion.
3:Annual Maintenance: Have a comprehensive maintenance check performed by a qualified technician. This may involve disassembling the lockout device for cleaning, lubrication, and calibration, if necessary. Keep detailed records of all inspections and maintenance activities to ensure compliance and traceability. -
What Is the Difference Between Valve Lockout and Tagout?
+While both are part of the LOTO process, there are significant differences:
1:Valve Lockout: Involves physically securing the valve with a mechanical lock to prevent operation. Only the person who applied the lock can remove it, providing a high level of security.
2:Valve Tagout: Uses warning tags, such as “Do Not Open” or “Do Not Close,” to indicate that the valve should not be operated. Tagout is used when a lockout device is not available or not technically feasible. However, tags alone rely on human compliance and are less secure than physical locks. OSHA requires lockout to be used whenever possible, as it offers a more positive means of preventing accidental valve operation. -
How Can You Ensure Your Facility Meets Valve Lockout Compliance During Audits?
+To prepare for audits:
1:Documentation: Maintain detailed written procedures for valve lockout for each valve type in your facility. Include diagrams, step-by-step instructions, and a list of approved lockout devices.
2:Training Records: Keep records of employee training on valve lockout procedures, including initial training and regular refresher courses. Training should cover the proper use of lockout devices, identification of hazards, and emergency procedures.
3:Inspection Logs: Keep a log of all lockout device inspections and maintenance activities. This helps demonstrate that your devices are in good working condition and regularly monitored.
4:Inventory Management: Maintain an up-to-date inventory of all valve lockout devices, noting their location, condition, and last inspection date. This ensures that you have the right devices available when needed.
5:Mock Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to identify any areas of non-compliance and address them before an official audit. This helps improve your overall safety program and increases the likelihood of passing audits successfully. -
What Should You Consider When Selecting a Valve Lockout Supplier?
+When choosing a supplier, look for the following:
1:Certifications: Ensure that the supplier’s products meet or exceed industry standards, such as OSHA, ANSI, and API requirements. Certifications provide assurance of product quality and safety.
2:Product Range: Choose a supplier that offers a wide variety of valve lockout devices to suit different valve types and sizes. This ensures that you can find the right device for your specific needs.
3:Quality and Durability: Look for lockout devices made from high-quality materials, such as stainless steel or heavy-duty plastic, that can withstand harsh industrial environments.
4:Customization Options: Some suppliers offer customized lockout solutions for unique valve configurations or specific safety requirements. This can be beneficial for facilities with specialized equipment.
5:Technical Support and Training: A good supplier should provide technical support and training resources to help you implement and maintain an effective valve lockout program. This may include installation guides, training videos, and on-site support. -
Can Valve Lockouts Be Used for Emergency Shutdowns?
+Can Valve Lockouts Be Used for Emergency Shutdowns?
Valve lockouts are primarily designed for planned maintenance and repair activities. While they can help prevent accidental valve operation during these tasks, they are not intended for emergency shutdowns. Emergency shutdown valves (ESDVs) are specifically designed to quickly isolate a process in case of an emergency, such as a fire, leak, or equipment failure. These valves are operated by dedicated emergency systems, such as remote controls or pressure sensors. However, after an emergency shutdown, valve lockouts can be used to secure the valves in their closed position during subsequent maintenance and repair work to ensure continued safety. -
What Are the Consequences of Not Using Valve Lockouts?
+Failure to use valve lockouts can have severe consequences:
1:Safety Risks: Workers may be exposed to hazardous substances, high-pressure fluids, or gases, leading to injuries, illnesses, or even fatalities.
2:Environmental Damage: Uncontrolled valve operation can result in spills, leaks, or emissions, causing pollution and harm to the environment.
3:Legal Penalties: Non-compliance with safety regulations such as OSHA can result in significant fines, citations, and legal liability for the facility and its management.
4:Operational Disruptions: Accidental valve operation can lead to process upsets, equipment damage, and production downtime, resulting in financial losses and missed deadlines. Implementing a proper valve lockout program is essential for protecting workers, the environment, and the bottom line of your business.