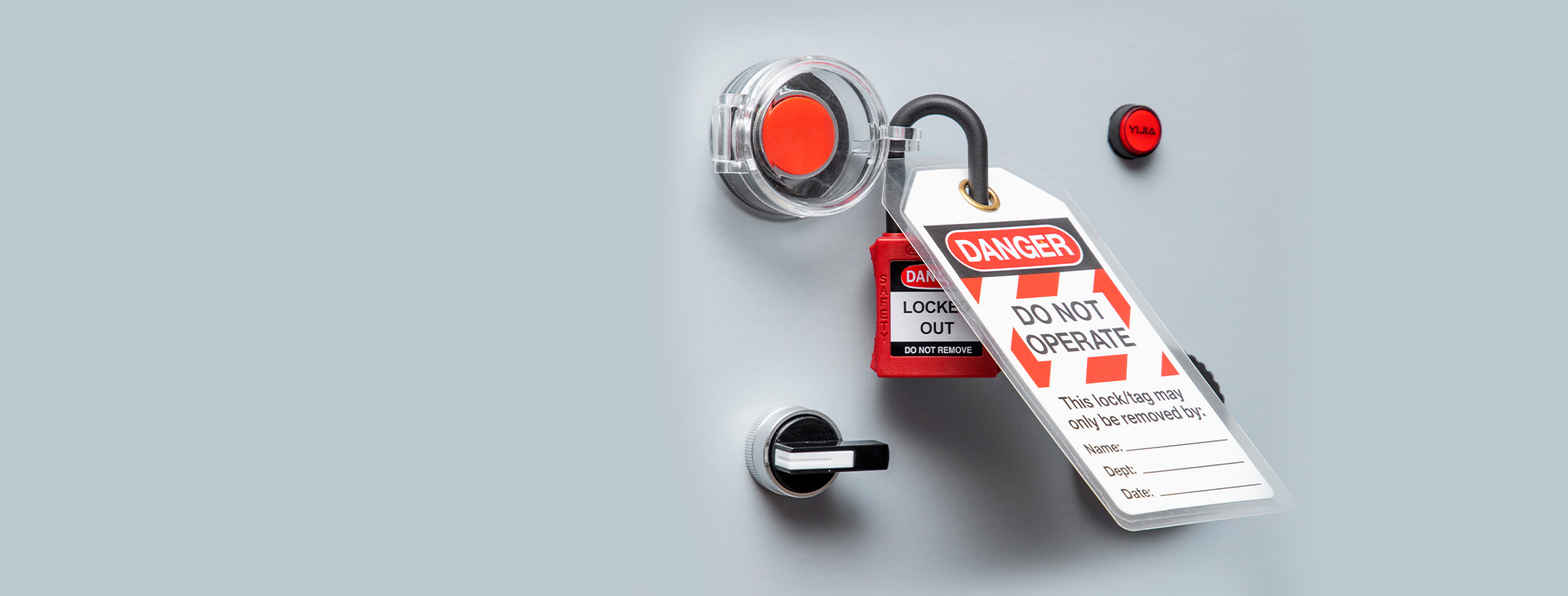
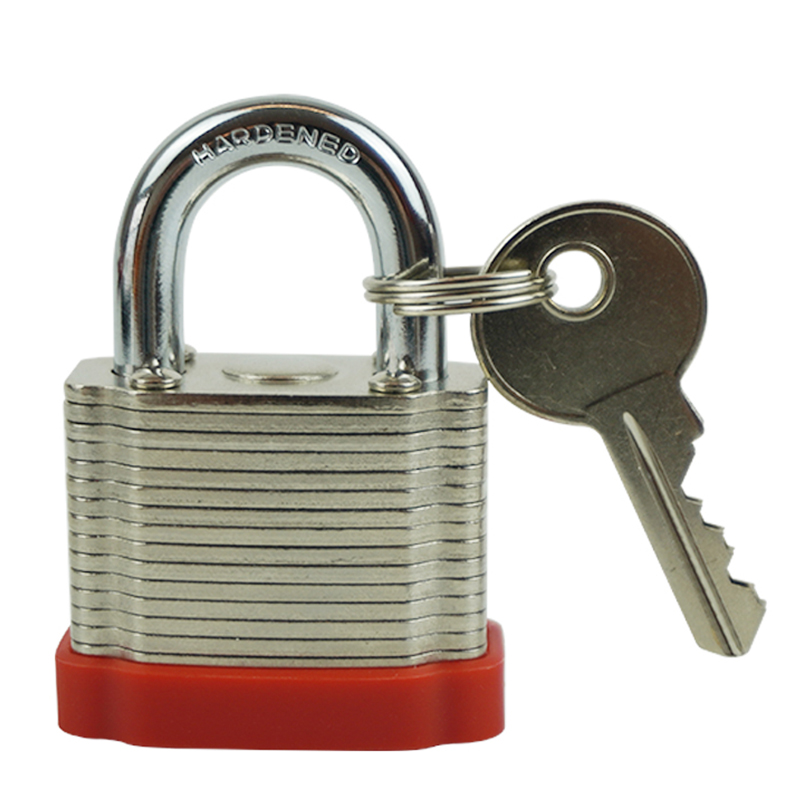
Lockout Padlocks
Electrical Equipment Lockouts are essential safety procedures used to prevent accidental or unauthorized activation of electrical equipment during maintenance, repairs, or servicing. By isolating and securing energy sources, lockouts help protect workers from hazards such as electric shocks, arc flashes, or equipment malfunctions.
-
EP-8581 Long body durable lockout padlock
LONG BODY SAFETY PADLOCKShackle Material:38MM Insulation Shackle
Inquiry -
EP-8551L High and low temperature resistance lockout padlocks
76MM Insulation Lockout Padlocks
Inquiry -
EP-8531N Slim body safety lockout padlocks
SLIM BODY SAFETY PADLOCKShackle Material:Slim insulation
Inquiry -
EP-8521N Laser printing impact resistance lockout padlocks
SLIM BODY SAFETY PADLOCKShackle Material:Slim 316 Stainess Stee
Inquiry -
EP-8541T Corrosion resistance lockout padlocks for equipment
CABLE PADLOCKShackle Material:Cable length 175mm, Cable dia: 1.5mm
Inquiry -
EP-8541 PA cable lockout padlocks
CABLE PADLOCKShackle Material:Cable length 175mm, Cable dia: 3.mm
Inquiry -
EP-8531 Easy to handle lockout padlocks for personnel safety
38MM Insulation Shackle padlock
Inquiry -
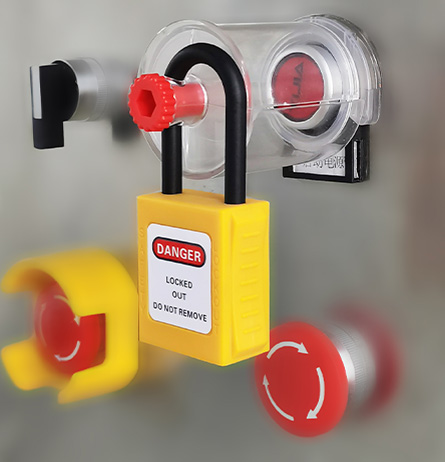
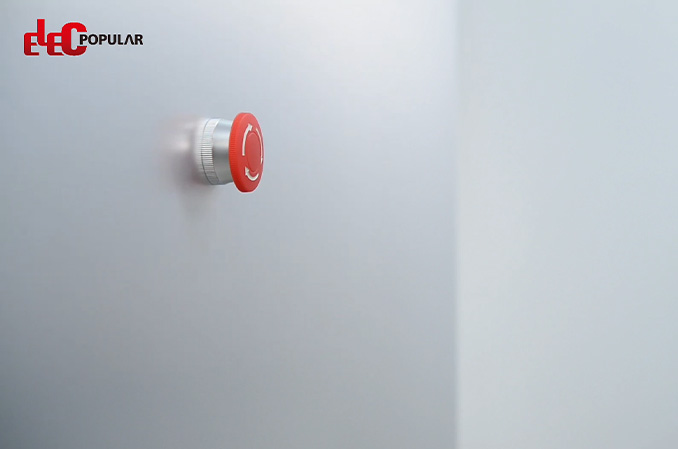
Pushbutton switch lockout Safety portable lockout padlocks
Electrical Equipment Lockouts are essential safety procedures used to prevent accidental or unauthorized activation of electrical equipment during maintenance, repairs, or servicing. By isolating and securing energy sources, lockouts help protect workers from hazards such as electric shocks, arc flashes, or equipment malfunctions.
Inquiry -
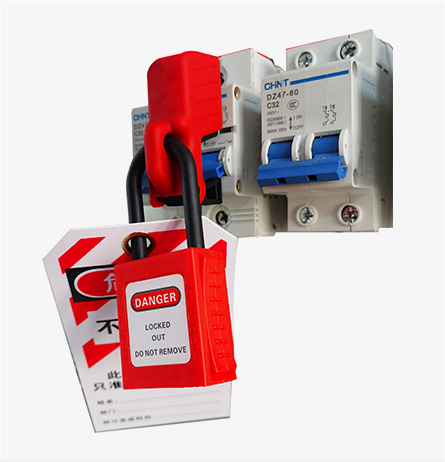
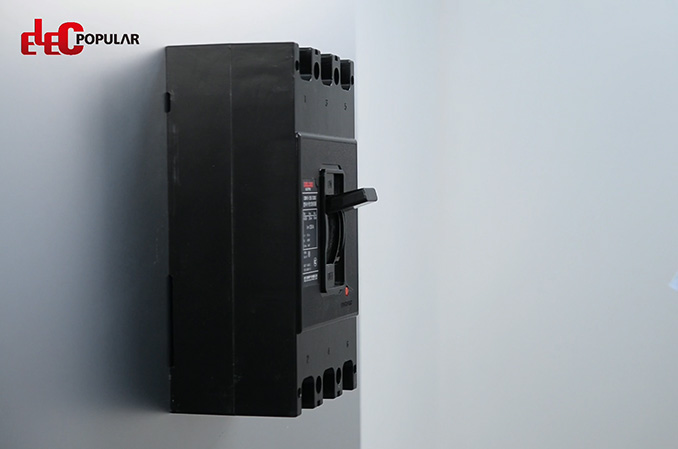
Breaker lockout Universal circuit lockout padlocks
Electrical Equipment Lockouts are essential safety procedures used to prevent accidental or unauthorized activation of electrical equipment during maintenance, repairs, or servicing. By isolating and securing energy sources, lockouts help protect workers from hazards such as electric shocks, arc flashes, or equipment malfunctions.
Inquiry -
EP-8521AP Key retaining lockout padlocks for safety protection
ALUMINUM BODY COATED PLASTIC SAFETY PADLOCK Material:38MM Steel coated Rubber shackle
Inquiry -
EP-8551AP Durable high-strength shackle lockout padlocks
ALUMINUM BODY COATED PLASTIC SAFETY PADLOCK Material:76MM Steel coated Rubber shackle
Inquiry -
EP-8521A Robust construction brass lockout padlocks
Aluminum padlock Material:38MM Steel Shackle
Inquiry -
EP-8511A lightweight lockout padlocks for personal belongings
Aluminum padlock Material:25MM Steel Shackle
Inquiry -
EP-B41 High-Capacity labels available lockout padlocks
Laminated steel padlocks Shackle Material:38MM Steel Shackle
Inquiry -
EP-8562 Weatherproof safety lockout padlocks
Laminated steel padlocks Shackle Material:38MM Steel Shackle
Inquiry -
EP-8561 OEM 5-pin cylinder lockout padlocks
Laminated steel padlocks Shackle Material:19MM Steel Shackle
Inquiry
PRODUCT VIDEO
-
E22
Lockout Tagout Padlocks and labels allow you to quickly id equipment, areas and padlocks with important lockout/tagout (LOTO) information. These are self-adhering high-performance labels that can withstand harsh environments, provide Master Key system and Grand Master Key system
-
E33
Lockout hasps are a valuable and convenient way to lockout an energy source ensuring that your worker's safety is never compromised. Our hasps are available in a variety of highly visible, labeled and nonconductive options. They are ideal for group lockout procedures and will help give your team the piece of mind that each energy source is properly isolated.
PRODUCT ADVANTAGES
-
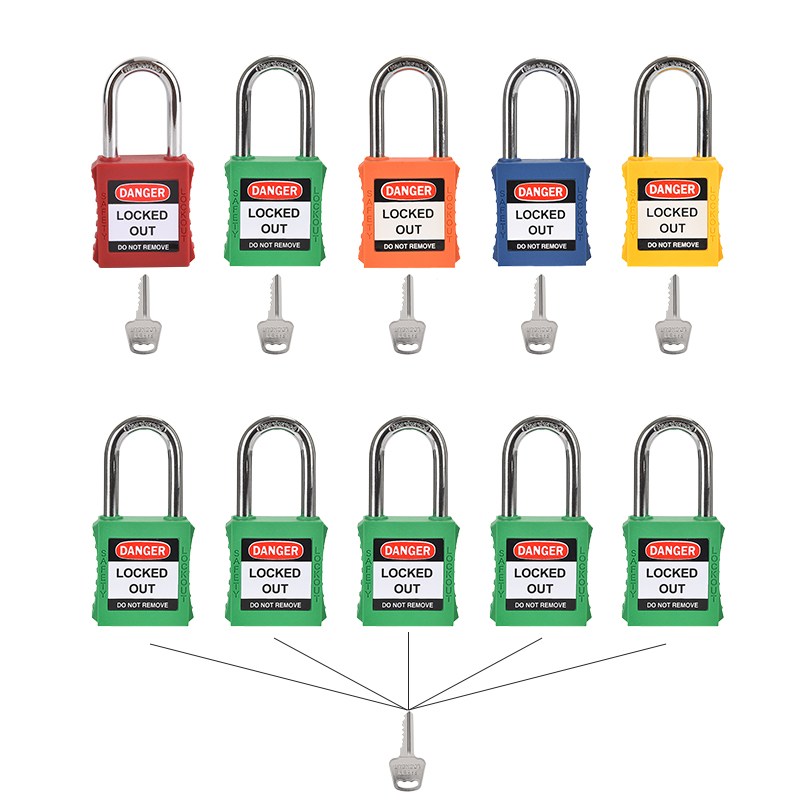
Unique Keycodes
Unique Keycodes
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
-
What is a safety padlock?
-A safety padlock is a lock specifically designed for use in Lockout Tagout (LOTO) procedures to secure energy isolation points during maintenance or servicing.
-
How is a safety padlock different from a regular padlock?
+Unlike standard padlocks, safety padlocks are non-conductive (if plastic), key-retaining, color-coded, and have unique key codes to prevent duplication. They are also lighter and often labeled for identification.
-
What materials are safety padlocks made from?
+Safety padlocks are commonly made from materials like:
1. Plastic (Nylon or Thermoplastic): Non-conductive and corrosion-resistant
2. Aluminum: Lightweight and durable
3. Steel: Heavy-duty applications (used with caution in electrical environments) -
What is a key-retaining feature?
+A key-retaining padlock does not allow the key to be removed unless the padlock is locked. This ensures the user doesn't leave it unlocked accidentally.
-
Why are safety padlocks color-coded?
+Color coding helps identify which worker owns the lock, or which department or type of hazard it relates to. This improves visibility, safety, and accountability.
-
Can multiple workers lock out the same equipment?
+Yes. A lockout hasp allows multiple padlocks to be applied to a single energy isolation point, so that each worker stays protected until their own lock is removed.
-
How many keys come with a safety padlock?
+Typically, each safety padlock comes with one unique key to maintain personal control and prevent unauthorized access.
-
Can I get replacement keys?
+Some safety padlock manufacturers offer key replacement services, but only under strict control. Most safety programs discourage replacement keys to maintain individual lock security.
-
Are safety padlocks available with key systems?
+Yes. Common keying systems include:
1. Keyed Different (KD): Each padlock has a unique key
2. Keyed Alike (KA): Multiple padlocks share the same key
3. Master Keyed (MK): Different padlocks with individual keys, but one master key can open them all. -
Where should safety padlocks be stored?
+Padlocks should be stored in a lockout station or shadow board in a clean, dry, and accessible location near the work area.