Electrical Equipment Lockouts
-
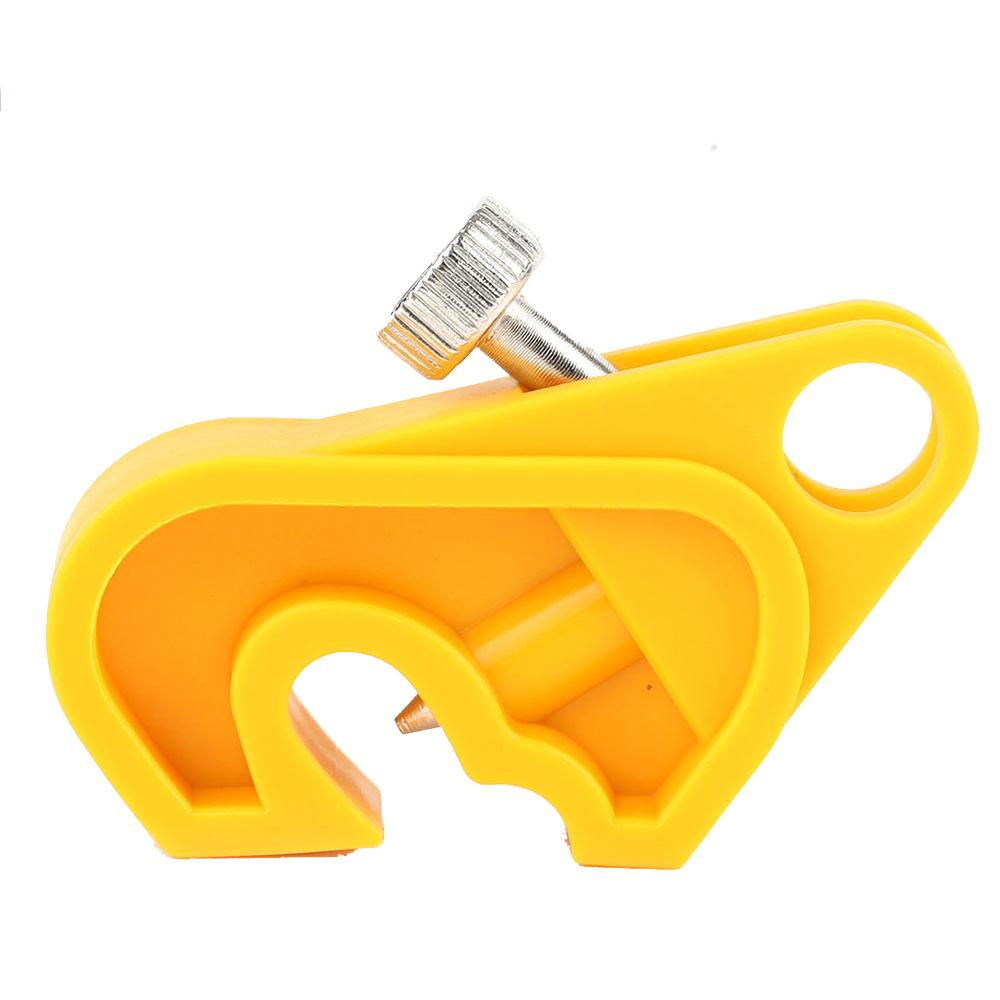
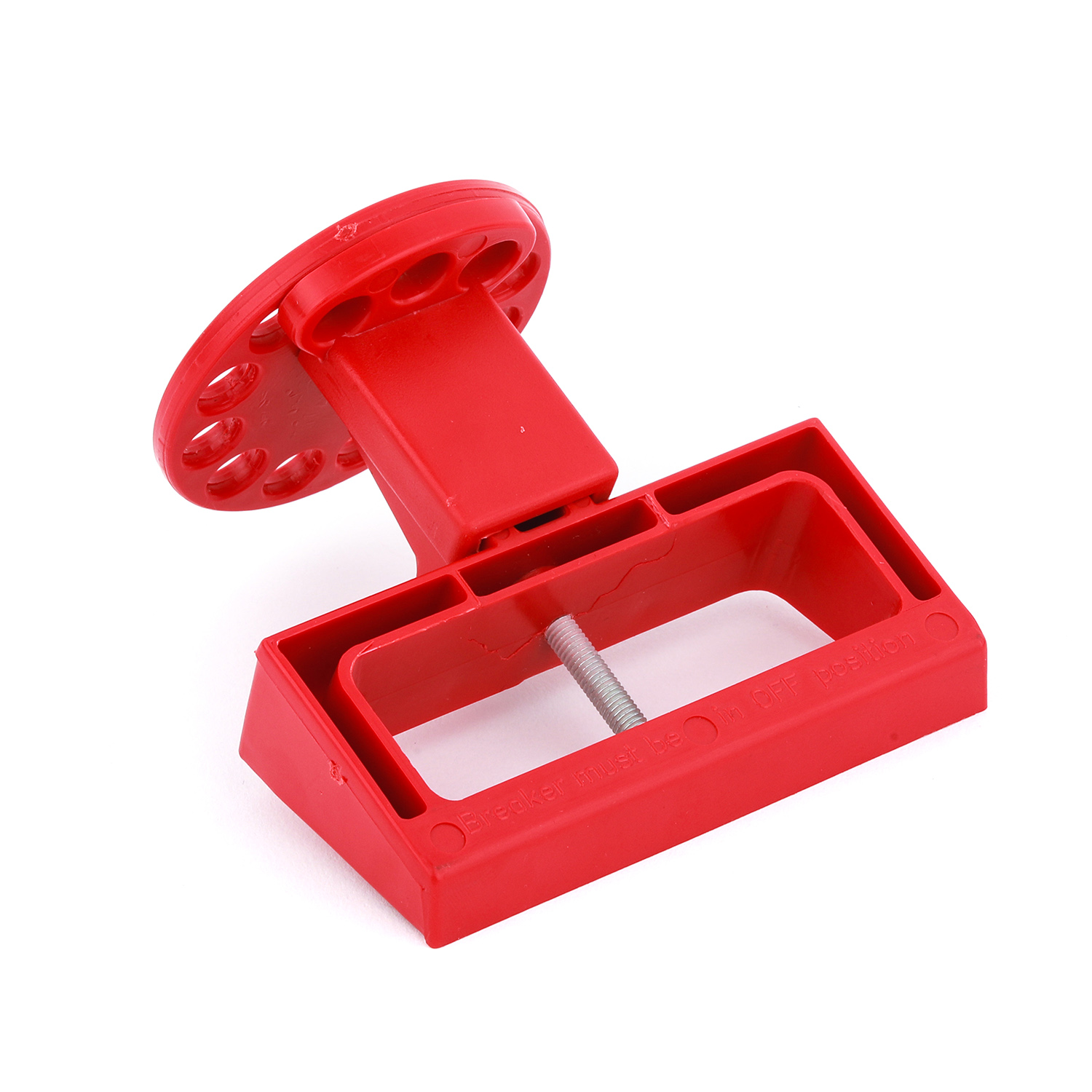
EP-D09N Circuit breaker electrical equipment lockouts with metallic nut
Material - High Quality ABS with metallic nut.Circuit Breaker Lockout with plain and folding screw type that is UV resistant.It fits on wide range of switches that is of 0.30" to 0.60" height suitable for single ,double, triple and four pole.Color - Yellow, Red or any color as per the quantity required.
Inquiry -
EP-D52A 30mm push-button electrical equipment lockouts for padlock shackles
Push Button Safety CoverPush-button safety covers prevent unauthorized use of push/pull and twist-release emergency equipment.The self-contained sticking function can permanently fix the lock cover on the control device, effectively preventing accidental touches.The device is captured by a rotary or push button switch bezel and has a clear base and cover that allows visibility of the nameplate and labels.Transparent cover with hinged door can stay open for easy access when not in use.The cover f
Inquiry -
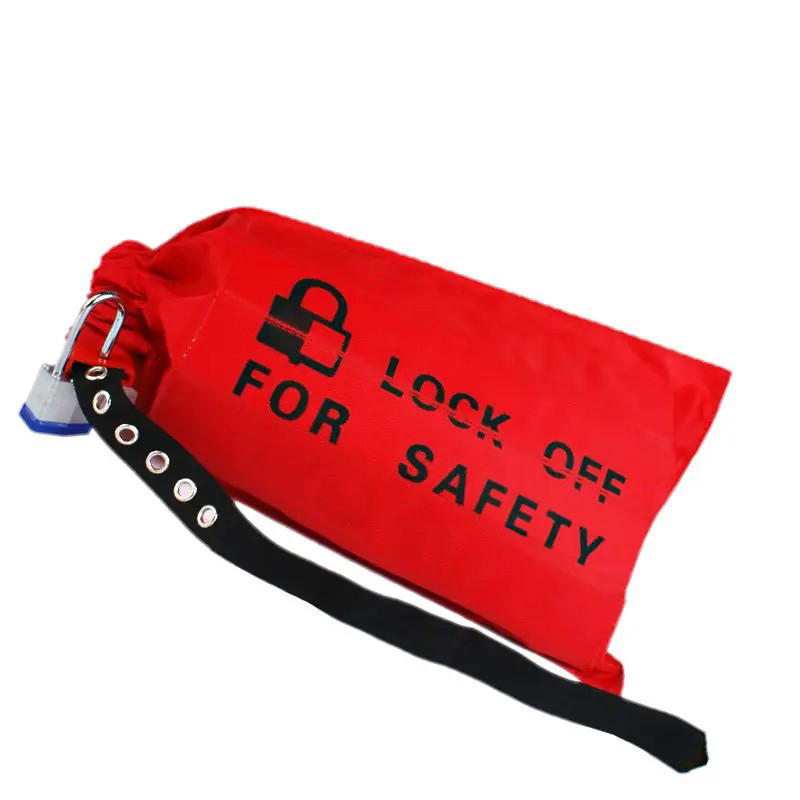
EP-D71/D71-2 Nylon bag electrical equipment lockouts for locking padlock
Crane/Hoist Control/Plug Lockout DevicesEffectively locks odd sized and large electrical connectors and lift controls, inserts PVC tubing to block access to lift control buttons.Flexible and durable ripstop nylon bag fits easily into a safety toolboxTrilingual “lock, do not remove” warning printed on the bag440*250MM/660*250MM/730*230mm three sizes, you can choose the appropriate size for locking padlock according to your needsIf the size specification can not meet your locking needs, please con
Inquiry -
EP-D42A Lightweight electrical equipment lockouts in tight space
The swivel electrical plug lockout surrounds a 120V or 220V electrical plug, preventing accidental reconnection during maintenance and repairs.Swivel design facilitates easier installation in tight space applications and is compatible with padlocks or hasps (sold separately).Strong, lightweight thermoplastic body helps resist chemicals and perform effectively in extreme conditions. It can be effectively locked to prevent misoperation.Includes a prominent permanent safety label.Works with most 11
Inquiry -
EP-D46 Practical industrial waterproof plug electrical equipment lockouts
Industrial Waterproof Plug LockoutFits standard plug sizes from 16a though to 125a Provides a simple means of effectively isolating access to plugs and adapters by stopping the plug from being inserted into an energy source. The plug-guard is ideal for maintenance personnel or anyone who wishes to stop accidental power connection whilst working on machinery in remote locations or during long term servicing. It can also be used to prevent usage of electrical equipment by unauthorised personnel. T
Inquiry -
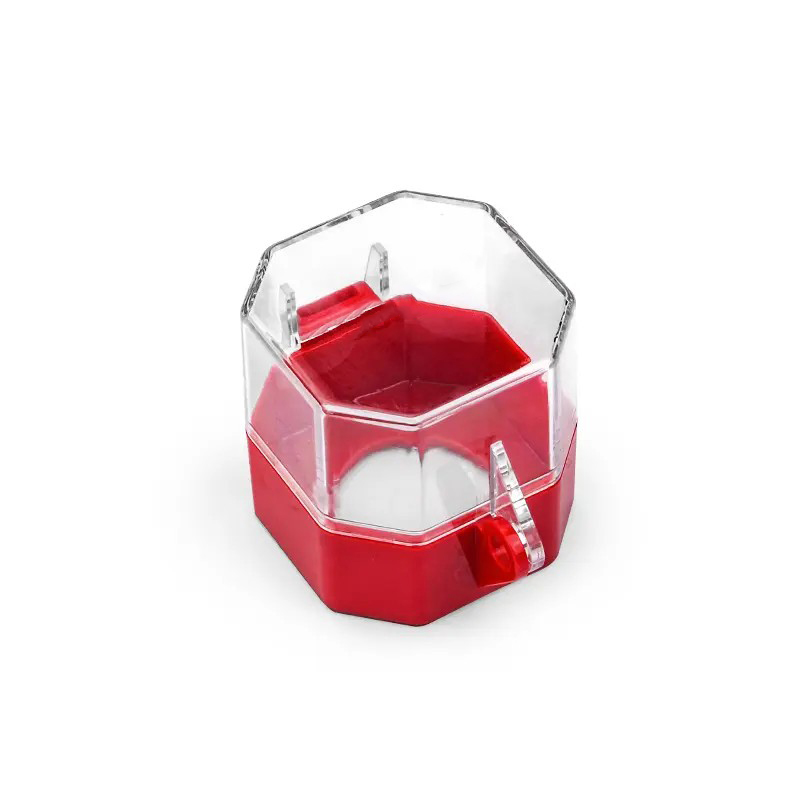
EP-D41/D42/D43 Polypropylene electrical equipment lockouts for industrial plugs
Hubbell Plug lockout boxThe Hubbell plug locking mechanism is designed to prevent the power plug from being inserted into the wall outlet, especially when the person performing service or maintenance is not the only person with access to the plug.It is suitable for most heavy duty industrial plug applications as part of an electrical safety Plug lockout boxDouble open and hexagon lockout design, accommodates a large variety of plug shapes and sizes.Constructed of rugged polypropylene.Includes a
Inquiry -
EP-D34 Swivel electrical equipment lockouts in extreme conditions
Hubbell Plug lockout boxThe Hubbell plug locking mechanism is designed to prevent the power plug from being inserted into the wall outlet, especially when the person performing service or maintenance is not the only person with access to the plug.It is suitable for most heavy duty industrial plug applications as part of an electrical safety and compliance program.Plug guards are great for maintenance personnel or anyone looking to stop accidental power connections when working on machines in rem
Inquiry -
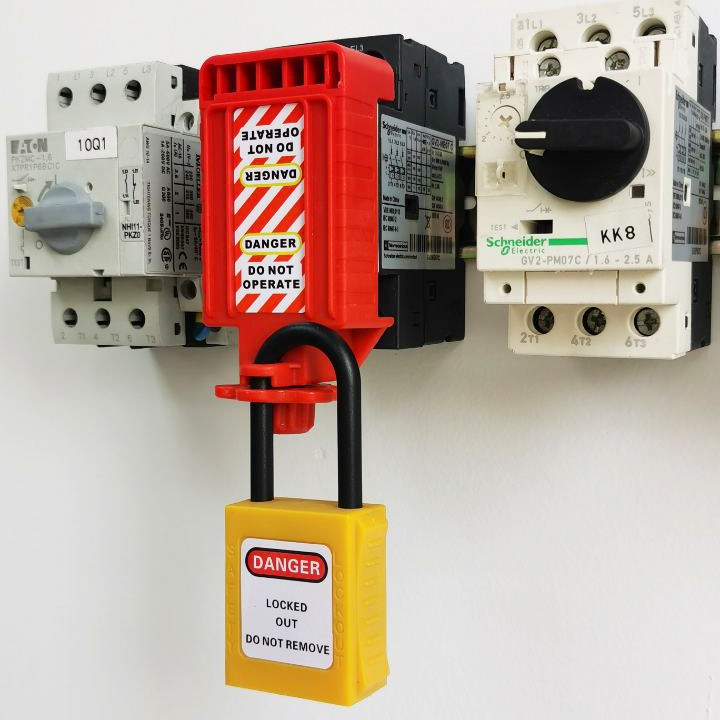
EP-D27 Effective electrical equipment lockouts for saving lives
Pin type circuit breaker lockout device is used to provide locking to the miniature circuit breaker that is with appropriate small holes, squeeze from the back to open the jaws of the lockout device and then fix or lock it properly in the hole of the MCB. Can be used for single pole circuit breaker, required no tools for installation.Material – Nylon, ABS, Metallic PIN and SpringIdeal for use on single pole MCB’sSuitable tor locking Schneider Electric Multi9 C60 miniature circuit breaker.MCB Pin
Inquiry -
EP-D30 Customized electrical equipment lockouts for small circuit breaker
The body is made from PBT.For locking small size circuit breakerThe lockouts can take padlock with a shackle diameter up to 8mm.Color: Yellow, can be customized
Inquiry -
EP-D28 Easily-installed yellow miniature circuit breaker electrical equipment lockouts
Circuit Breaker Lockout for SchneiderYellow Miniature Circuit Breaker Lockout is specially made for Schneider Circuit Breakers.Easily installed,no tools needed.Can take padlocks with a shackle diameter up to 6.5mm. Can be installed on single/multi-pole breakers.Padlock must be installed for lockout
Inquiry
PRODUCT ADVANTAGES
-

Perforated cable lock
Product model: EP- C15
Description: Lock single or multiple adjacent switches. After the key is pulled out, the steel cable can still be tightened infinitely, and multiple people can be locked at the same time. -

Circuit breaker lock
Model: EP-E26
Description: Mainly used for locking motor/motor circuit breaker switches
Features:
1. Made of reinforced nylon, strong and durable
2. Metal tooth clamping design, more stable locking
3. Loosen/tighten by hand, fast locking
4. Locking length: 41-57mm, width 38mm, height 22mm -

Button switch lock
Product model: EP-E39
Description: It can lock button switches with labels and various button switches at close range -
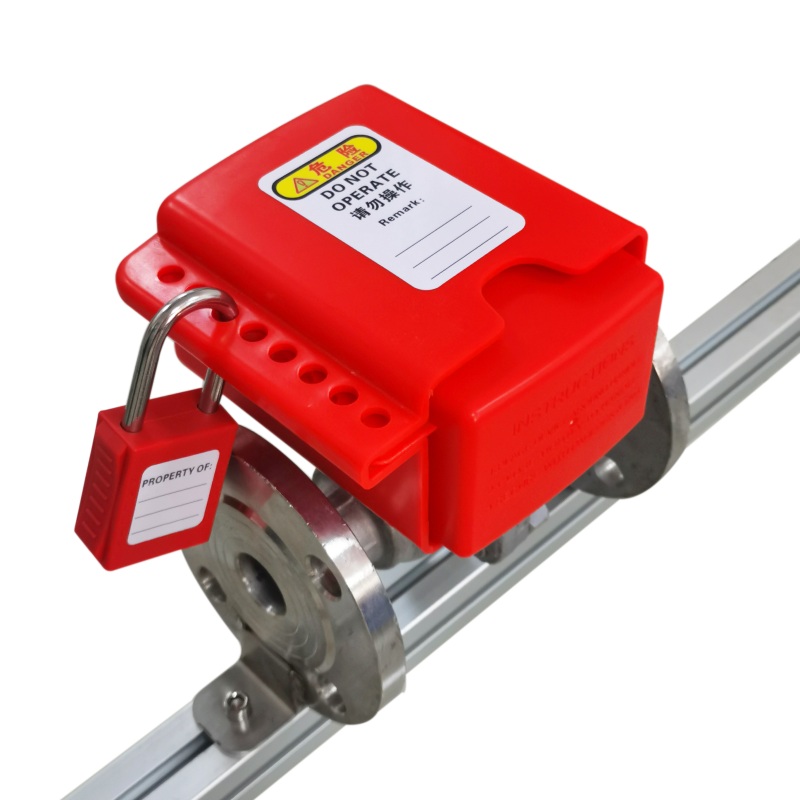

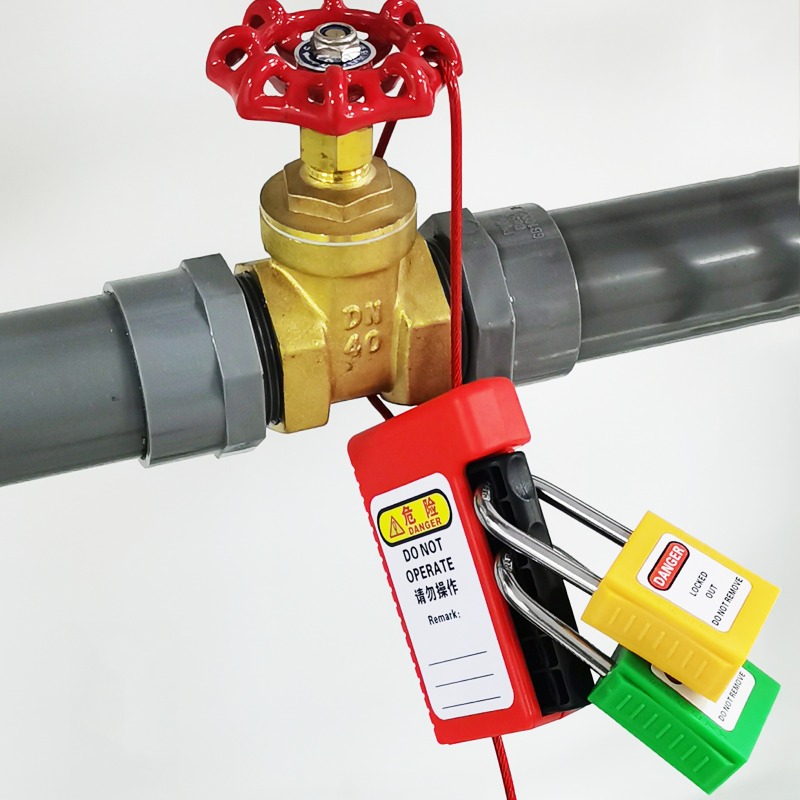
Plug valve lock
Model: EP-V42
Description: Mainly used for locking flanged ball valves/plug valves
Features:
1. Made of engineering plastics, light and tough
2. Simple structure and easy operation
3.8 hole design is easier to adjust and lock
4. Locking range: <DN150 -
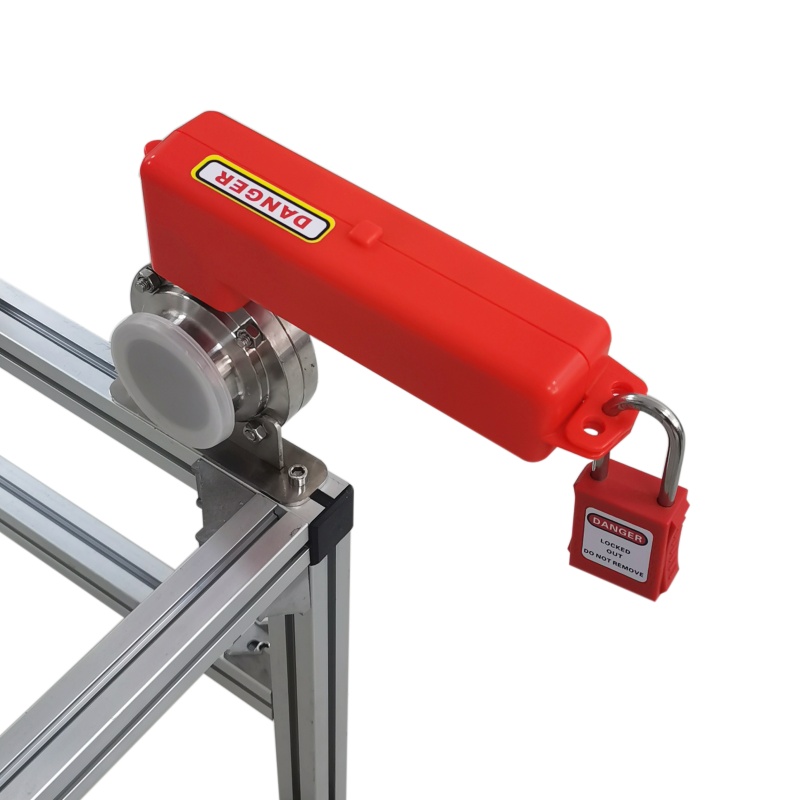

Sanitary butterfly valve lock
Model: EP-V24
Description: Mainly used for locking sanitary butterfly valves
Features:
1. Made of engineering plastics, strong and durable
2. Patented package structure design, easy to lock and easy to operate
3. It can lock most of the existing sanitary butterfly valves
4. With 2 diameter 8mm and 1 diameter 6.5mm upper lock holes -
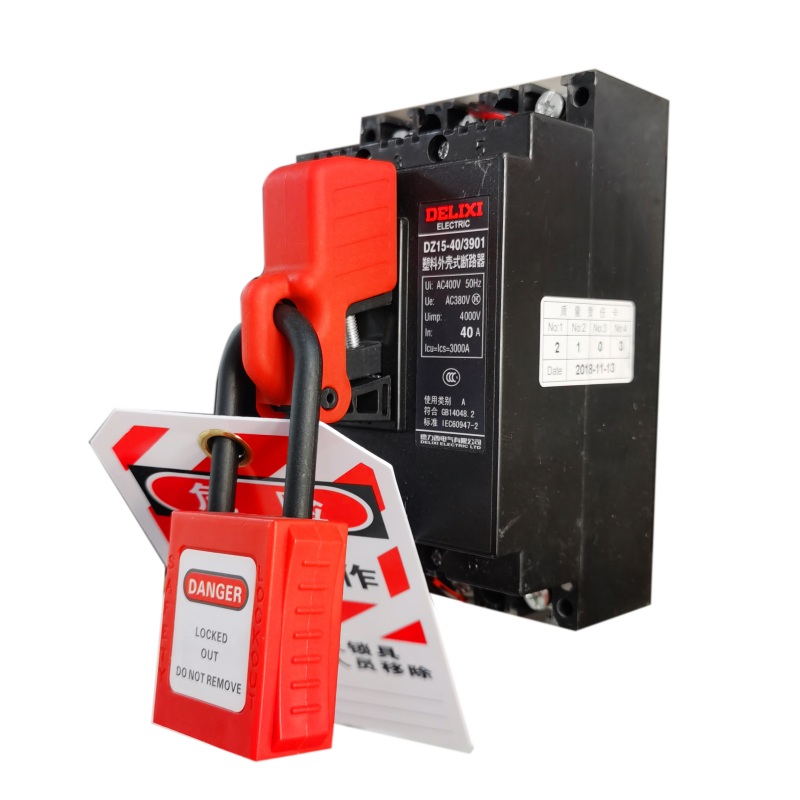

Multifunctional circuit breaker lock
Name: multifunctional circuit breaker lock
Model: EP-E15A
Description: It can not only lock the miniature molded case circuit breaker switch but also lock the miniature circuit breaker switch. -
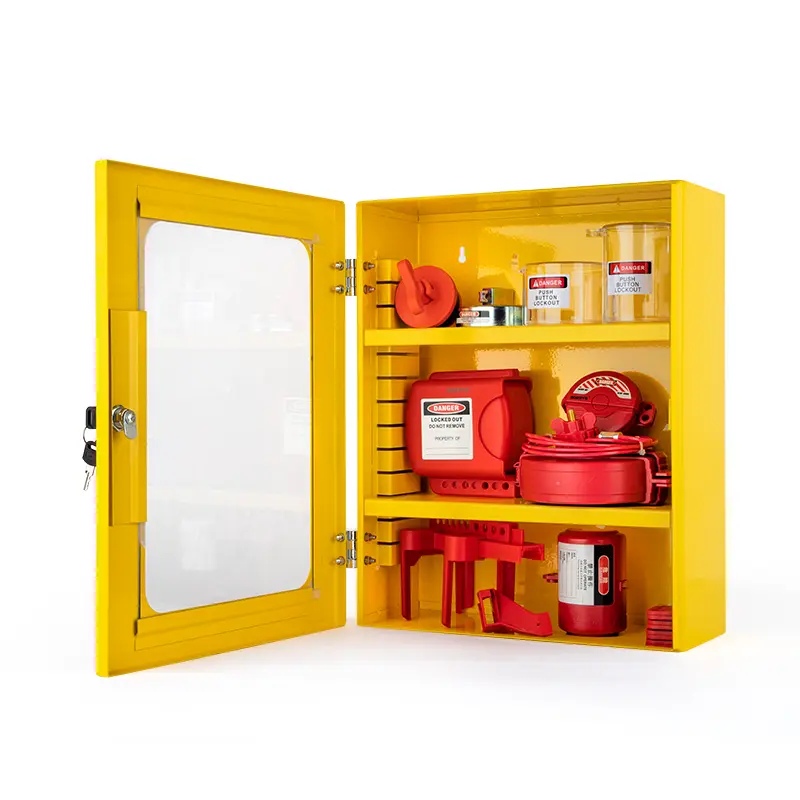

Lockout tagout stations
Model No.: EP-X07
The Lockout tagout stations size:width × height × thickness: 360mm × 450mm × 155mm,With two mobile division plates, can set the division space flexibly. -
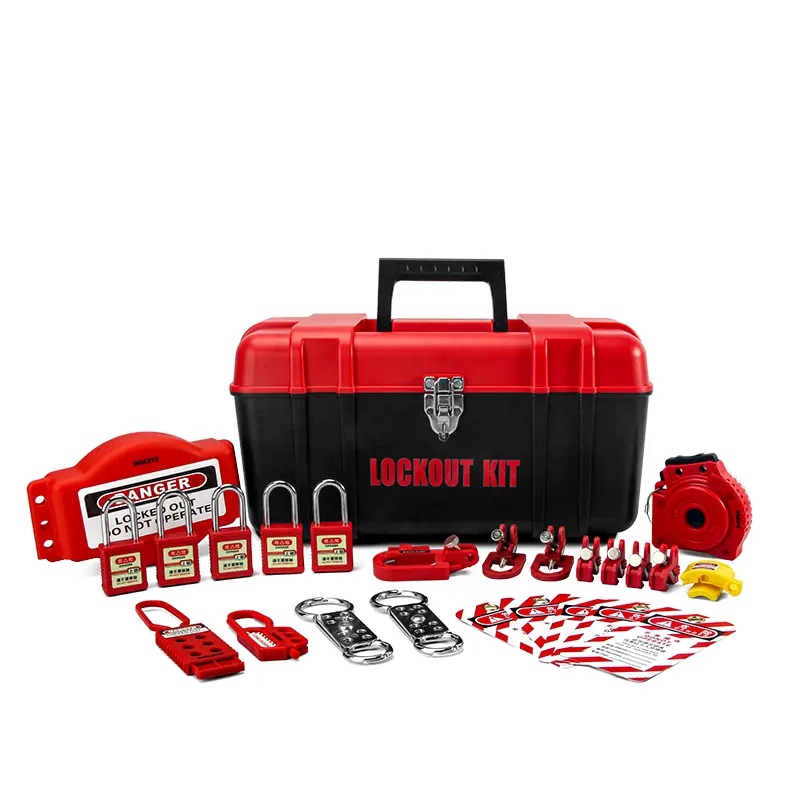

Lockout tagout kits
Lockout Tagout Kits includes:
Safety padlock *1 set
1 set of lockout box
1 set of miniature circuit breaker lockout
1 set of clamp breaker lockout
1 set of 6 holes lockout hasp
1 pcs Aluminum lockout hasp,plug lockout
1 set of emergency stop lockout
Safety Tag
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
-
What Are Electrical Equipment Lockouts and Why Are They Important?
-Electrical equipment lockouts are safety procedures designed to isolate machinery or equipment from its energy source(s) before maintenance, repair, or servicing. This involves physically locking switches, circuit breakers, or other energy-isolating devices to prevent accidental startup. Lockouts are critical for compliance with OSHA (29 CFR 1910.147) and NFPA 70E standards, reducing risks of electric shock, arc flash, or mechanical injury. By ensuring zero energy state, lockouts protect workers from unexpected energization, a leading cause of industrial accidents.
-
What Are the Key Standards for Electrical Lockout Procedures?
+The primary regulatory standards include:
1:OSHA Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Standard (1910.147): Mandates controlling hazardous energy during servicing, requiring written procedures, employee training, and periodic inspections.
2:NFPA 70E (Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace): Focuses on electrical safety practices, including lockout requirements for de-energizing equipment before work.
3:ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems): Encourages systematic lockout protocols as part of hazard prevention. Compliance ensures legal adherence and minimizes liability while fostering a safety-first culture. -
How Do I Properly Implement an Electrical Lockout Procedure?
+Follow these steps for effective lockout:
1:Prepare: Identify all energy sources (electrical, mechanical, hydraulic) and relevant lockout devices.
2:Notify: Inform all affected workers about the upcoming lockout.
3:Shut Down: Power down equipment using normal shutdown procedures.
4:Isolate: Disconnect energy sources and apply lockout devices (e.g., circuit breaker locks, switch locks).
5:Verify: Test for zero energy using voltage testers or other appropriate tools.
6:Control: Assign individual locks with unique keys to authorized workers.
7:Release: Remove locks only after confirming all work is complete and the area is safe.Document each step and train employees regularly to ensure consistency. -
What Types of Lockout Devices Are Used for Electrical Equipment?
+Common lockout devices include:
1:Circuit Breaker Locks: Secure breakers in the "off" position, preventing unauthorized resetting.
2:Disconnect Switch Locks: Fit over manual disconnect switches to block operation.
3:Plug Lockouts: Prevent re-connection of power plugs during maintenance.
4:Universal Lockout Hasps: Allow multiple workers to lock a single energy source (group lockout).
5:Tagout Devices: Though not a substitute for locks, tags warn against energizing locked-out equipment. Choose devices rated for the specific voltage and equipment type, ensuring compatibility with safety standards. -
How Often Should Electrical Lockout Devices Be Inspected and Maintained?
+Regular inspections are vital for reliability:
1:Daily Checks: Visually inspect locks for damage or misalignment before use.
2:Monthly Inspections: Test functionality (e.g., latch mechanism on circuit breaker locks).
3:Annual Maintenance: Conduct thorough checks per manufacturer guidelines, replacing worn components.Document inspection results and replace devices at the first sign of wear—cracked plastic, rusted metal, or loose fittings can compromise safety. OSHA requires lockout equipment to be "substantially durable" and maintained in good condition. -
What's the Difference Between Lockout and Tagout in Electrical Safety?
+While both are part of LOTO procedures:
1:Lockout: Uses physical locks to prevent equipment energization; only the worker who applied the lock can remove it (unless under authorized procedures).
2:Tagout: Uses warning tags (e.g., "Do Not Energize") when locking isn't feasible. Tags alone are less effective as they rely on visual recognition rather than physical restriction.OSHA requires lockout over tagout whenever possible, as locks provide a higher level of protection against accidental startup. Tagout is permitted only when locks aren't technically feasible, but additional precautions (e.g., multiple tags, supervisor approval) are necessary. -
How Can I Ensure My Facility Meets Lockout Compliance During Audits?
+To prepare for audits:
1:Document Procedures: Maintain written lockout protocols for each piece of equipment, including energy source locations and step-by-step instructions.
2:Training Records: Keep records of employee training (initial and refresher courses, at least every three years per OSHA).
3:Inspection Logs: Track device maintenance and periodic inspections.
4:Compliance Kits: Use standardized lockout kits with clearly labeled devices for quick access.
5:Mock Audits: Regularly review processes for gaps, such as missing locks on redundant energy sources.A compliant program reduces audit failures, penalties, and most importantly, workplace incidents. -
What Should I Look for When Choosing an Electrical Lockout Supplier?
+Select suppliers who offer:
1:Certifications: Products compliant with OSHA, NFPA, and ISO standards.
2:Product Range: Diverse solutions for circuit breakers, switches, plugs, and custom applications.
3:Durability: High-quality materials (e.g., corrosion-resistant steel, impact-resistant plastic) for industrial environments.
4:Ease of Use: Ergonomic designs for quick application and removal, reducing downtime.
5:Support Services: Training resources, technical documentation, and responsive customer service.Reliable suppliers ensure your lockout system is both 6:effective and adaptable to evolving equipment needs. -
Can Lockout Procedures Be Used for Emergency Shutdowns?
+Lockouts are primarily for planned maintenance, but emergency shutdowns (e-stop buttons, pull cords) serve a different purpose:
1:Emergency Shutdowns: Quickly de-energize equipment in unsafe situations but don't replace lockouts for maintenance.
2:Lockout Follow-Up: After an emergency shutdown, follow standard lockout procedures (isolate, lock, verify) before any work begins.Never rely solely on emergency stops for maintenance—they may not fully disconnect all energy sources or prevent accidental resetting. -
What Are the Consequences of Not Using Electrical Lockout Procedures?
+Non-compliance risks include:
1:Safety Hazards: Increased chance of electric shock, arc flash burns, or mechanical injuries.
2:Legal Penalties: OSHA fines up to $13,653 per serious violation, plus potential criminal charges for willful non-compliance.
3:Downtime: Accidents can halt operations, leading to production losses and reputational damage.
4:Insurance Issues: Denied claims for incidents resulting from inadequate safety protocols.Investing in proper lockout procedures is a proactive way to protect workers, assets, and business continuity.