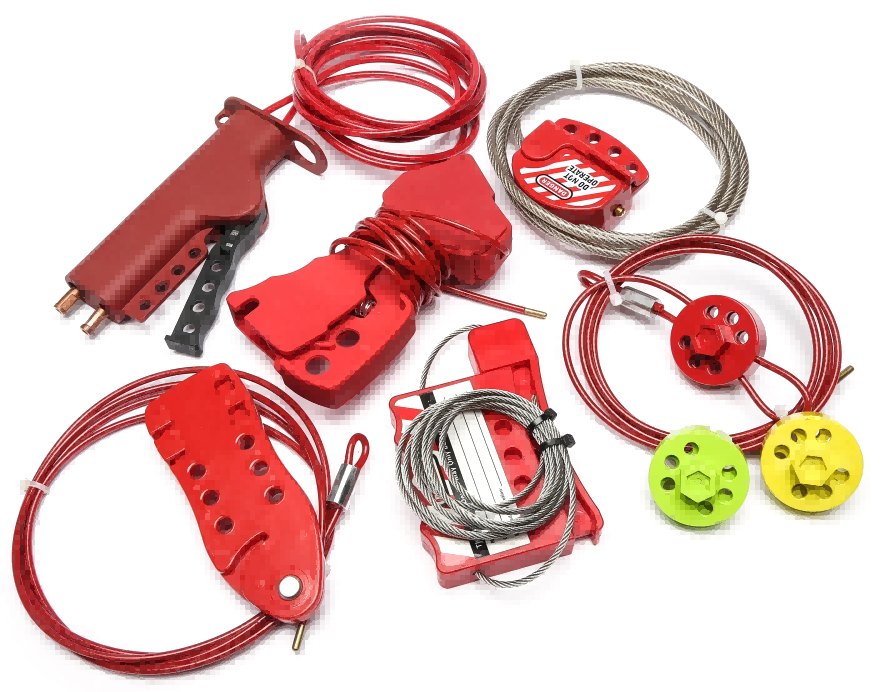
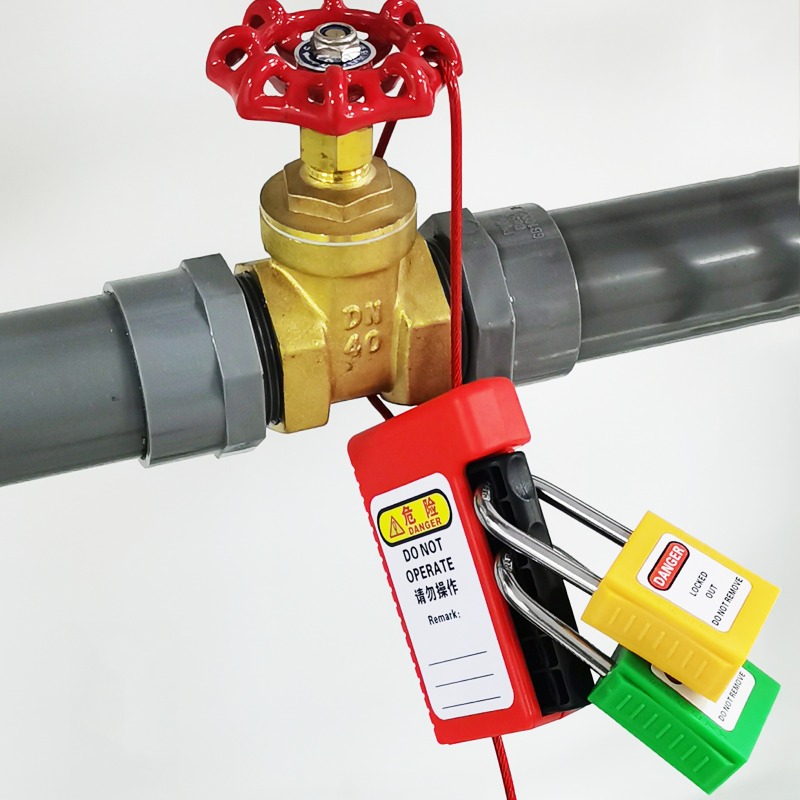
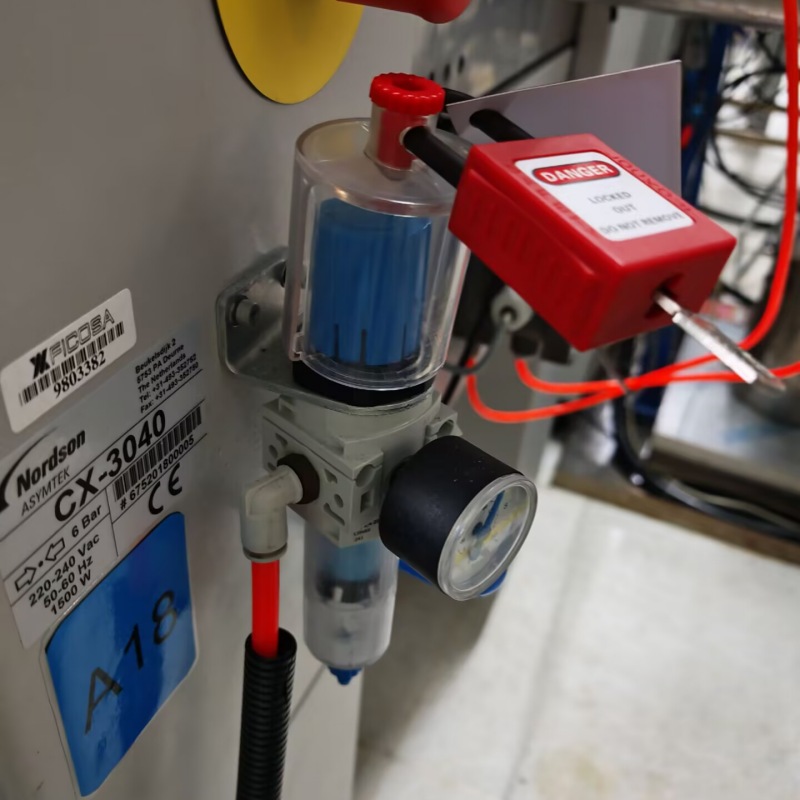
Cable Lockouts
-
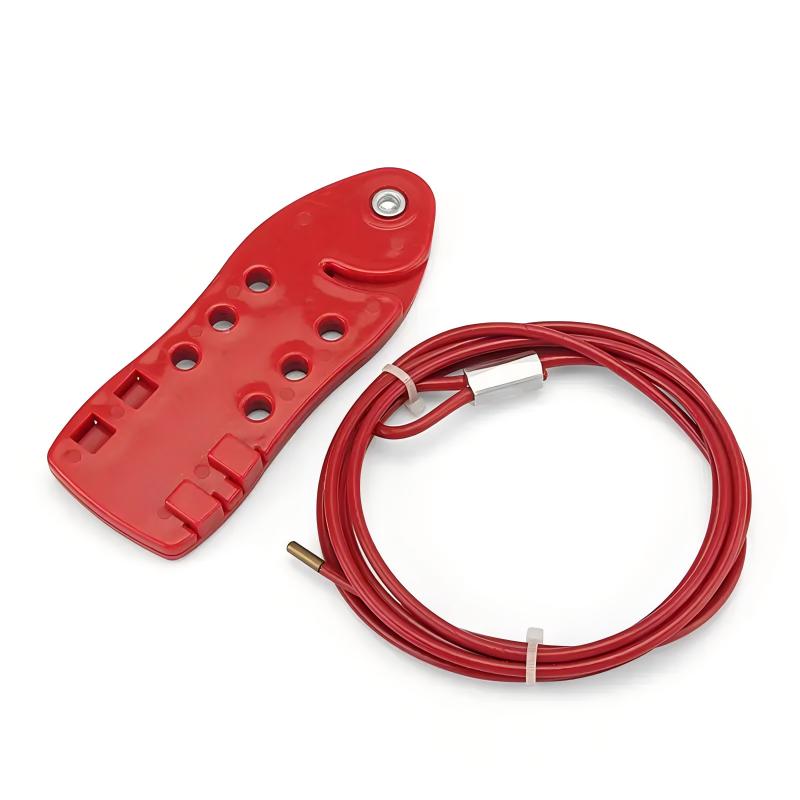
EP-L01 Grip cable lockouts irregular equipment
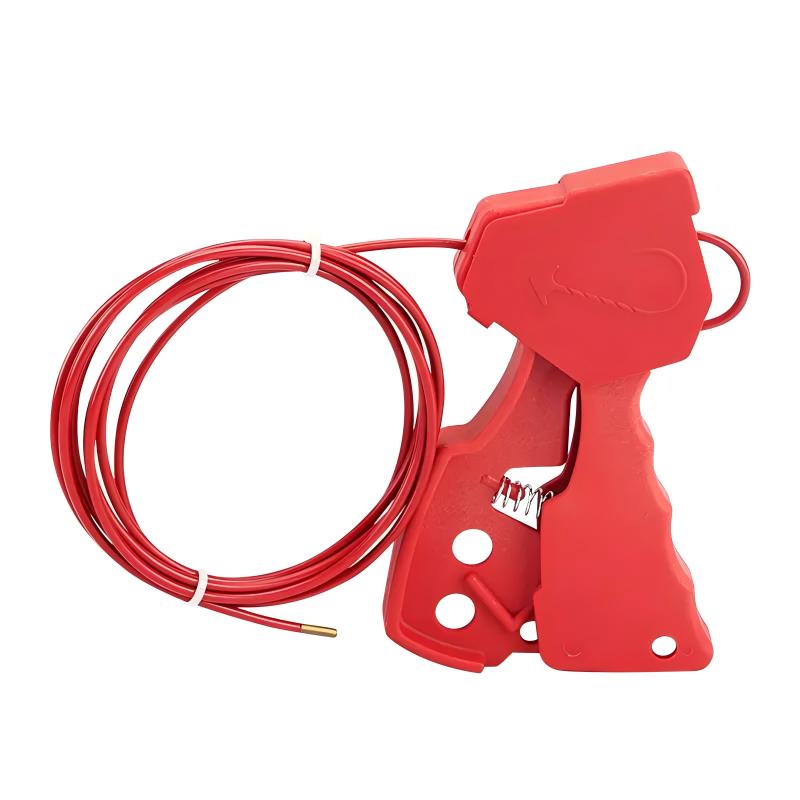
Grip Cable LockoutGrip Cable Lockout Device with 3.5MM*2.4m Stainless Steel CableGrip Cable Lockout locks are a versatile energy isolation solution ideal for unusual installations that cannot be locked with traditional equipment.The Grip Cable Lockout has an insulating coating of PVC with transparent UV protection and a multi-stranded stainless steel cable inside, which can effectively lock irregular equipment.The 2-hole design allows multiple people to lock and manage hazards at the same time.T
Inquiry -
EP-L11 Adjustable cable lockouts four lock holes
●Made from impact resistant engineering plastic PC, can be customized other colors.●Used 1.8 meter cable, the outer layer of cable is made from anti-UV PVC( diameter 6mm), the cable can be customized with deffirent length and color ●With Extra temperature of -46℃ -149℃●Locked wirh 4 padlock, lock shackle diameter is less than 7mm
Inquiry -
EP-L02 Adjustable cable lockout device for unusual equipment
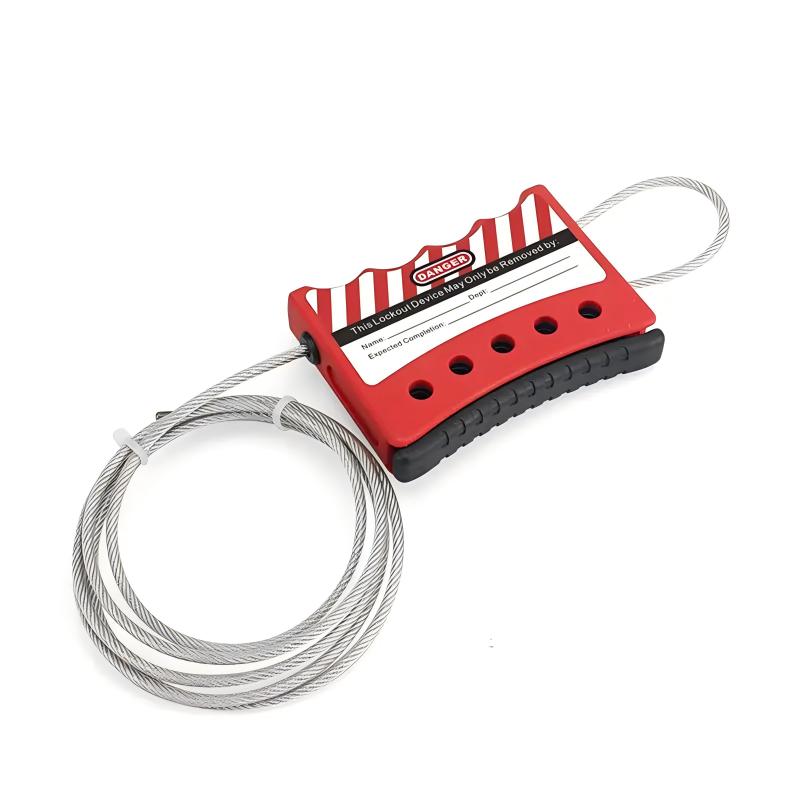
Cable LockoutsAdjustable cable lockout device with 4MM*1.8m tension cableThe adjustable cable lockout is a versatile energy isolation solution for use, ideal for unusual equipment that cannot be locked with traditional equipment.It has a transparent insulating coating with transparent UV protection and a multi-strand stainless steel cable inside, which can effectively lock irregular equipment.The 5-hole design can satisfy multiple people to lock and manage the danger source at the same time.The
Inquiry -
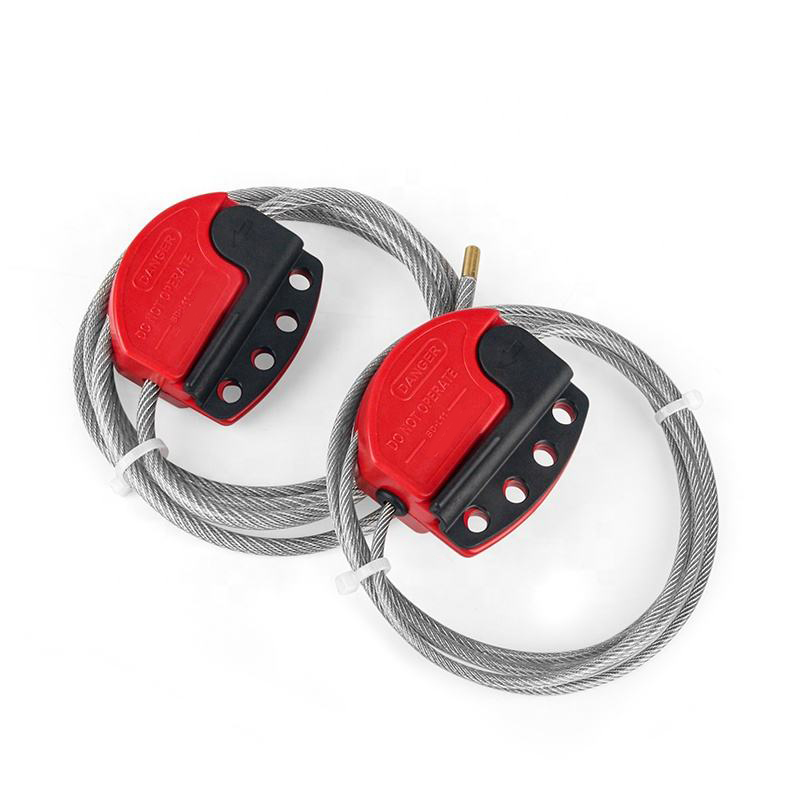
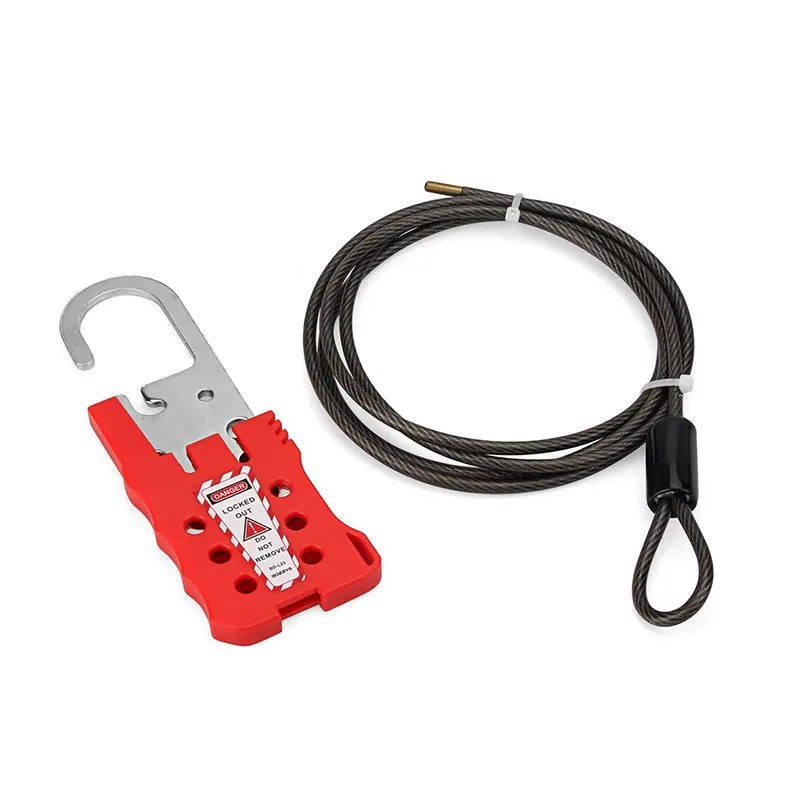
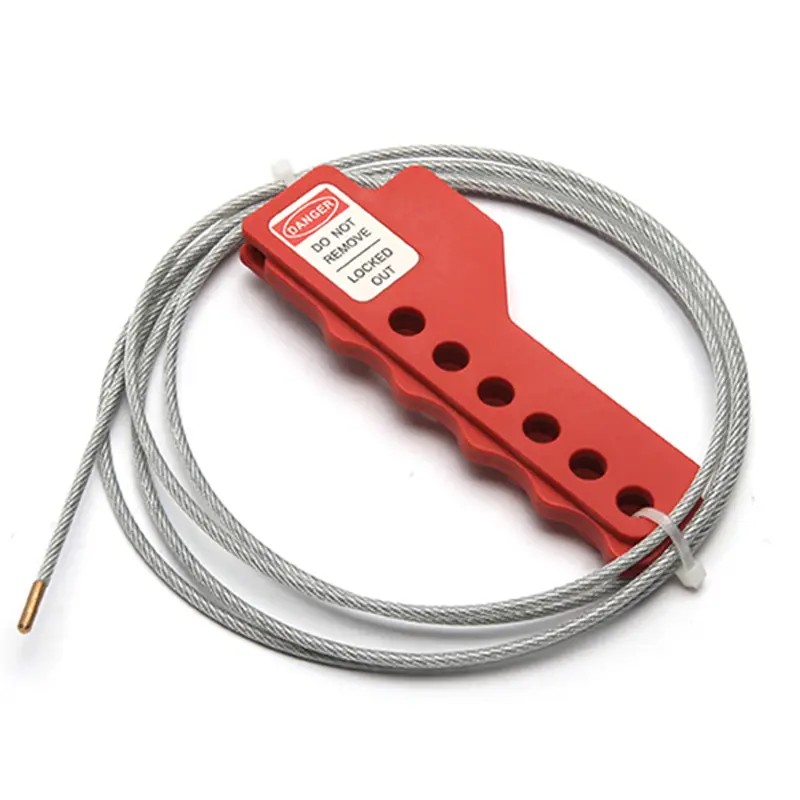
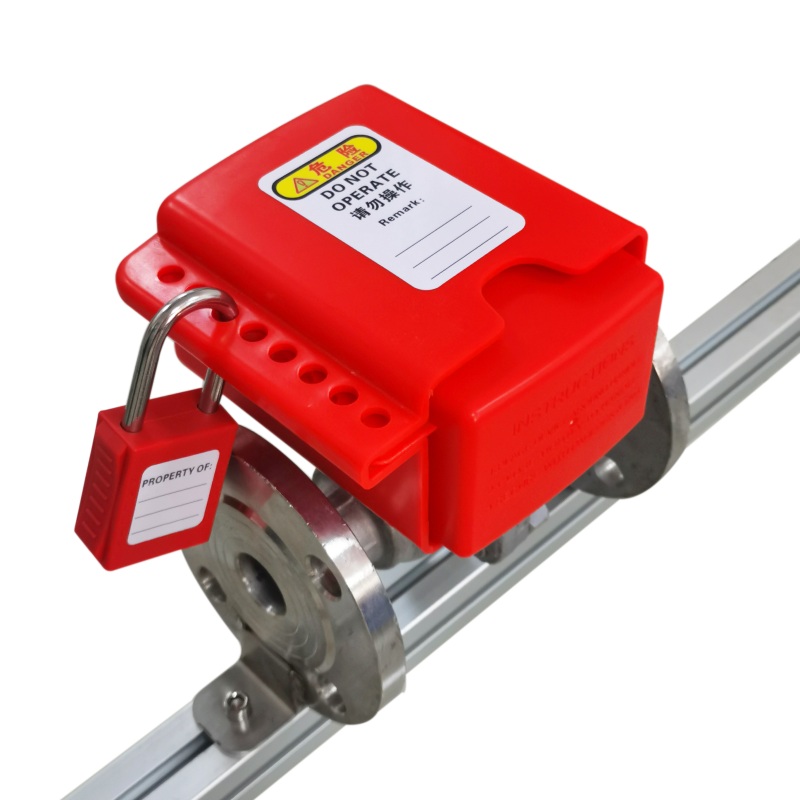
EP-L21 Economy cable lockouts with 2m stainless steel cable
Economy Cable LockoutThe Economy Cable Lockout Device from BOZZYS is constructed of impact modified nylon abs.The Economy Cable Lockout EP-L21 comes with a 2m stainless steel cable with an outer layer of UV resistant PVC (Cable diameter 4mm).Economy Cable Lockouts have 6 lock holes in the handle to accommodate most lock shackles and hasps.Equipping your employees with the proper lockout tools and warning devices can save lives, reduce lost employee time, and cut insurance costs.Economy Cable Loc
Inquiry -
EP-L22 6-hole design impact-modified glass-filled nylon cable lockouts
Multipurpose Cable Lockoutsmulti-purpose cable lockout with 4.8MM*1.8M PVC Coated Steel CableAll-Purpose Cable Lockouts is a versatile energy isolation solution for use, ideal for unusual equipment that cannot be locked with traditional equipment.All Purpose Cable Lockout bodies are made of rugged impact-modified glass-filled nylon for superior chemical, corrosion and temperature resistancecable Device comes complete with 4.8MM*1.8M PVC Coated Steel Cable attachmentLocks out multiple control poi
Inquiry -
EP-L51 All purpose cable lockout with 8' sheathed cable
Cable LockoutsAdjustable cable lockout device with 4MM*1.8m tension cableThe adjustable cable lockout is a versatile energy isolation solution for use, ideal for unusual equipment that cannot be locked with traditional equipment.It has a transparent insulating coating with transparent UV protection and a multi-strand stainless steel cable Cable lockouts are incredibly versatile making them perfect for all of your unusual energy isolating devices that are difficult to lock out. Compact, lightweig
Inquiry -
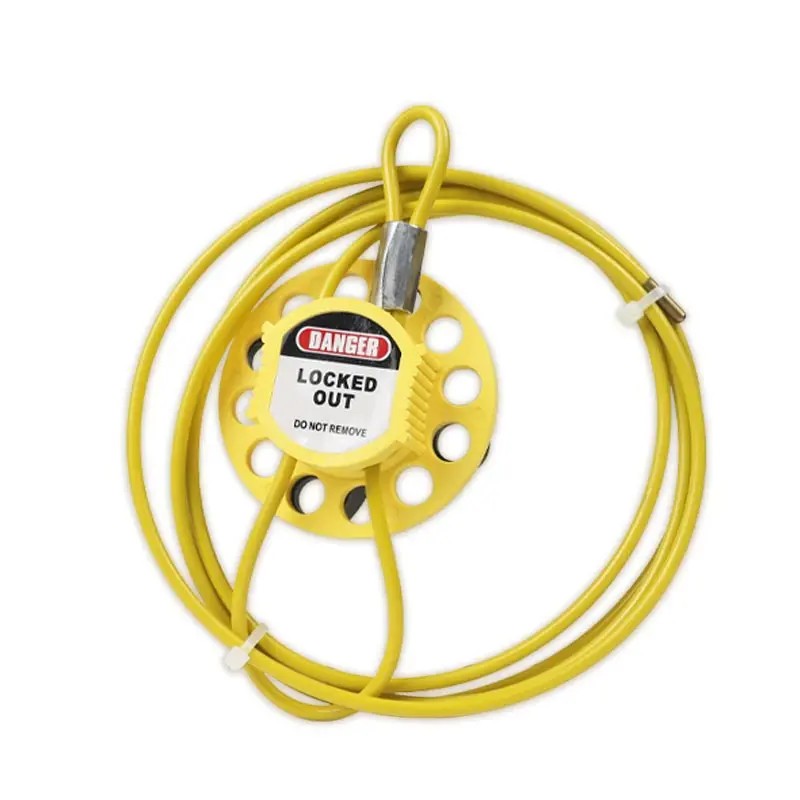
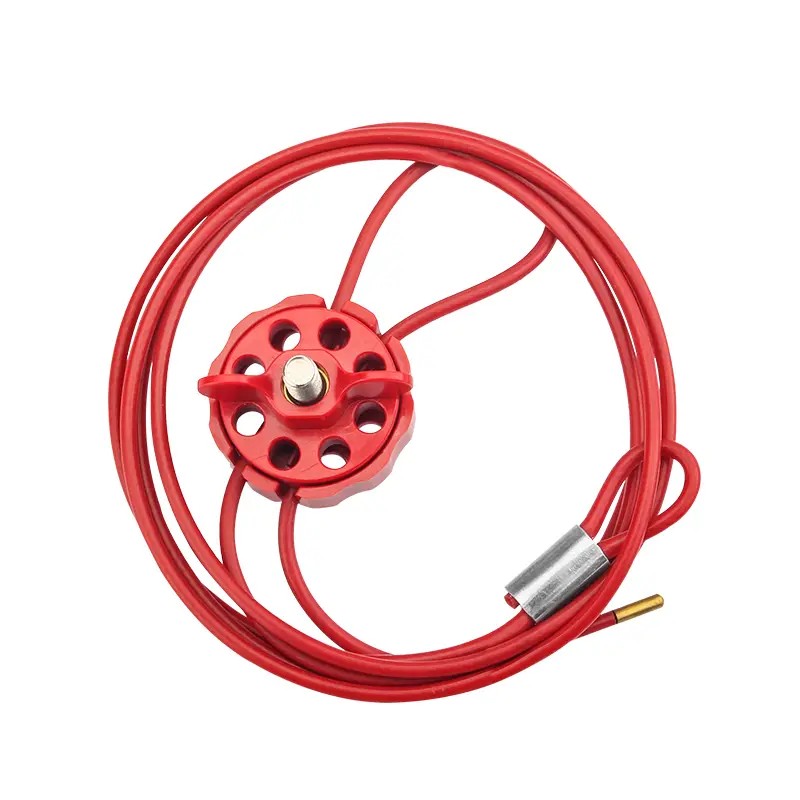
EP-L32 Cable lockout system for unusual equipment
Round Multipurpose Cable Lock 4MM*2M Stainless Steel CableSelf-locking handwheel, no tools requiredInnovative design, one-shot injection molding, concave and convex all around the lock body, butterfly-shaped rotating disc, ergonomic, high friction, more convenient to tighten and useFor attaching installed equipment for cable lockout systemadjustable multi-purpose Wheel Cable Lockout is a versatile energy isolation solution for use, ideal for unusual equipment that cannot be locked with tradition
Inquiry -
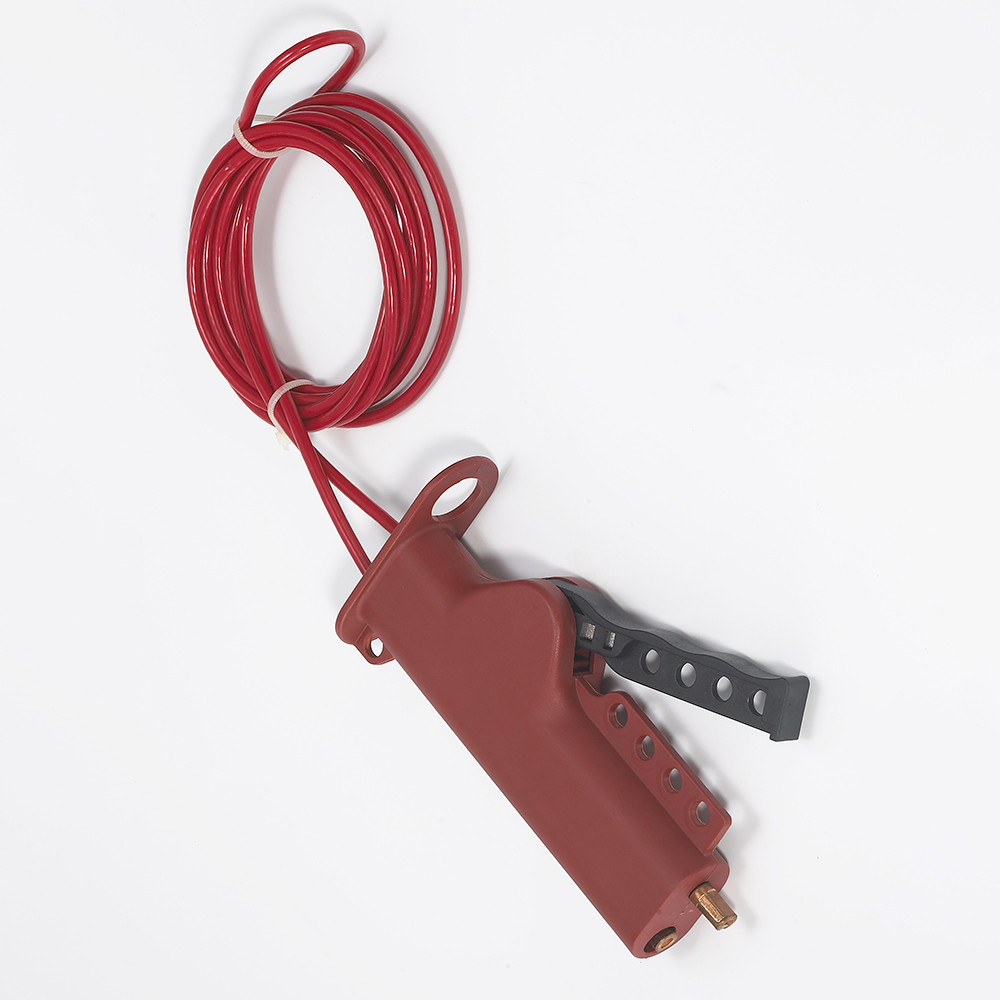
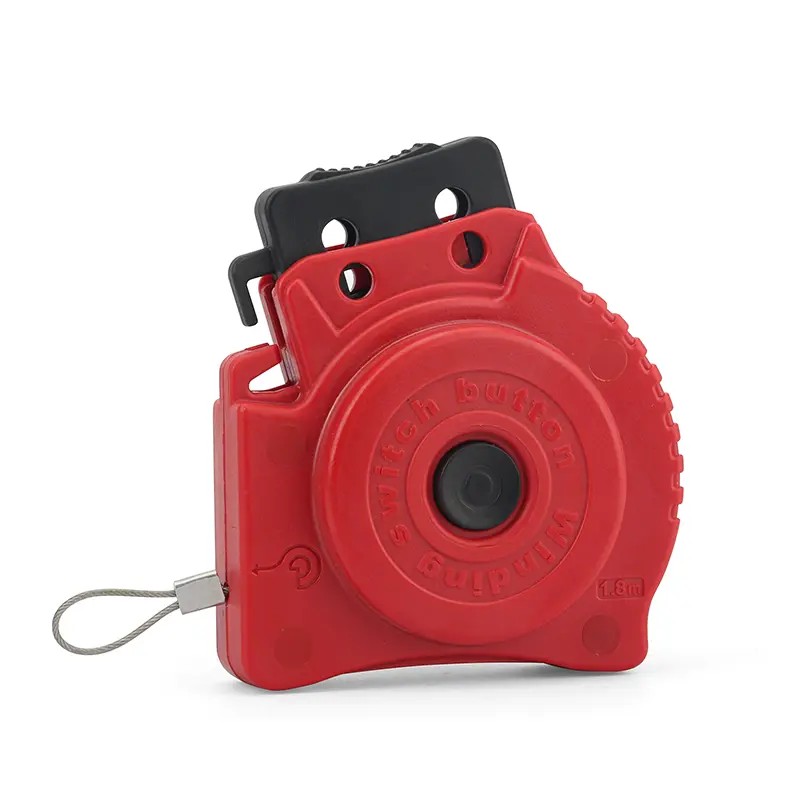
EP-L41 Retractable cable lockout device for irregular equipment
Cable Lockout DevicesRetractabl Cable Lockout Device with 2MM*1.8m Stainless Steel CableRetractable cable lockout device with 2MM*1.8m Stainless Steel cable management system,cable has an insulating coating of PVC with transparent UV protection and a multi-stranded stainless steel cable inside, which can effectively lock irregular equipment.Retractable Cable Lockout Devices are ideal for multi-point locking and group lockout, It’s a versatile energy isolation,solution ideal for unusual installat
Inquiry -
EP-L31 Self-locking handwheel one-shot injection molding cable lockouts
Round Multipurpose Cable Lock 4MM*2M Stainless Steel CableSelf-locking handwheel, no tools requiredInnovative design, one-shot injection molding, concave and convex all around the lock body, butterfly-shaped rotating disc, ergonomic, high friction, more convenient to tighten and useFor attaching installed equipment for safety, the equipment is made of upper and lower parts – both parts have holes 8 holesABS or polypropylene and metal parts, made of standard steel with external threads.The bolts
Inquiry -
EP-L61 Customized squeezer multipurpose cable lockouts
Squeezer Multipurpose Cable Lockoutadjustable cable lockout is a versatile energy isolation solution for use, ideal for unusual equipment that cannot be locked with traditional equipment.Cable accessories can be equipped with 3MM*1.8M PVC anti-ultraviolet coated steel cable, or 4MM*1.8M insulated cable, and the cable length can be customized. Ideal for multi-position locking of valve equipment and electrical switchgear.The pull-wire lock has a 6-hole design, and the lock can accommodate up to 6
Inquiry
PRODUCT ADVANTAGES
-

Perforated cable lock
Product model: EP- C15
Description: Lock single or multiple adjacent switches. After the key is pulled out, the steel cable can still be tightened infinitely, and multiple people can be locked at the same time. -
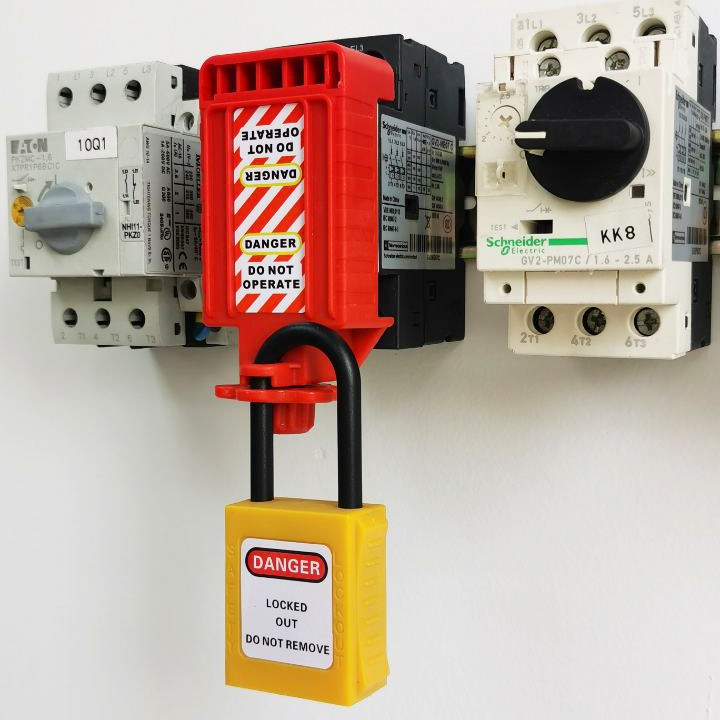

Circuit breaker lock
Model: EP-E26
Description: Mainly used for locking motor/motor circuit breaker switches
Features:
1. Made of reinforced nylon, strong and durable
2. Metal tooth clamping design, more stable locking
3. Loosen/tighten by hand, fast locking
4. Locking length: 41-57mm, width 38mm, height 22mm -

Button switch lock
Product model: EP-E39
Description: It can lock button switches with labels and various button switches at close range -

Plug valve lock
Model: EP-V42
Description: Mainly used for locking flanged ball valves/plug valves
Features:
1. Made of engineering plastics, light and tough
2. Simple structure and easy operation
3.8 hole design is easier to adjust and lock
4. Locking range: <DN150 -
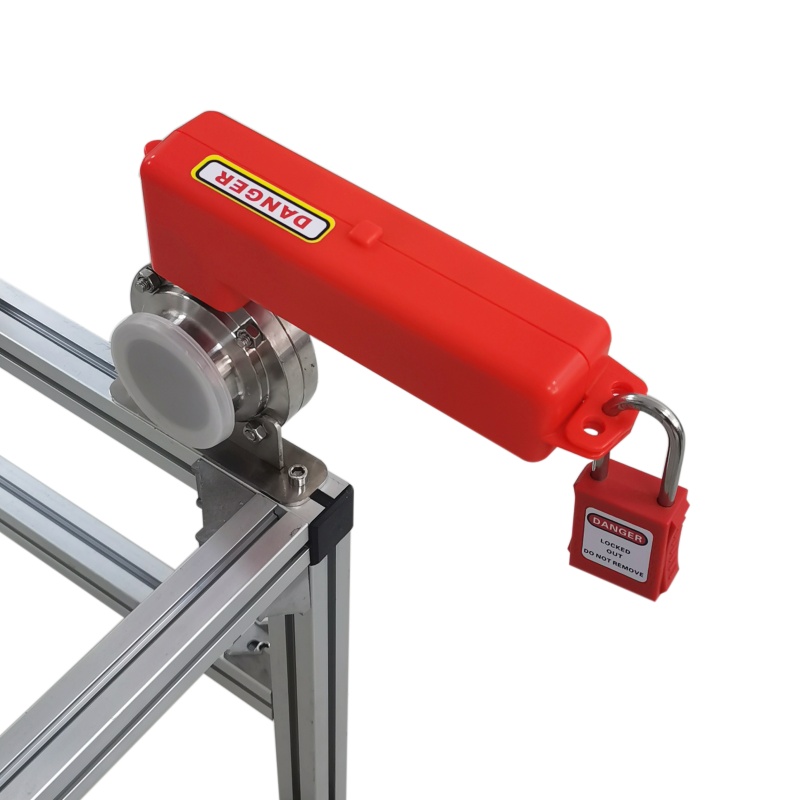

Sanitary butterfly valve lock
Model: EP-V24
Description: Mainly used for locking sanitary butterfly valves
Features:
1. Made of engineering plastics, strong and durable
2. Patented package structure design, easy to lock and easy to operate
3. It can lock most of the existing sanitary butterfly valves
4. With 2 diameter 8mm and 1 diameter 6.5mm upper lock holes -
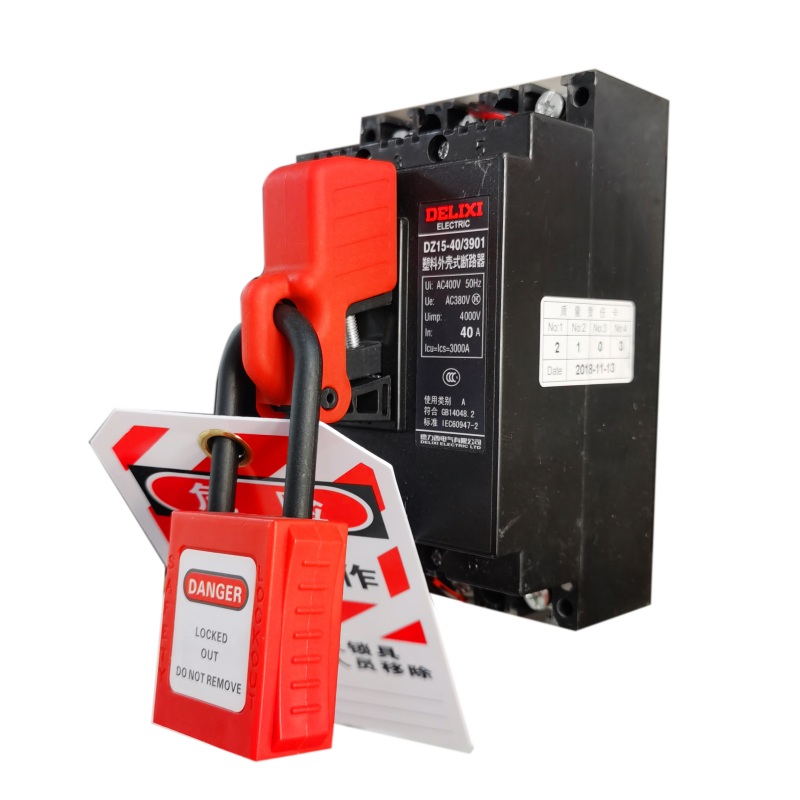

Multifunctional circuit breaker lock
Name: multifunctional circuit breaker lock
Model: EP-E15A
Description: It can not only lock the miniature molded case circuit breaker switch but also lock the miniature circuit breaker switch. -
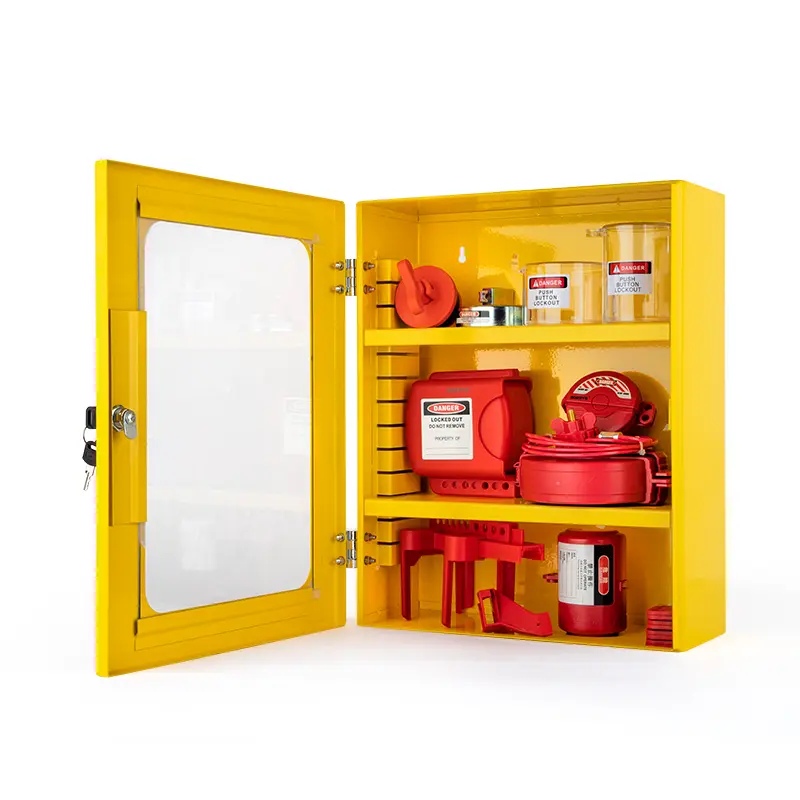

Lockout tagout stations
Model No.: EP-X07
The Lockout tagout stations size:width × height × thickness: 360mm × 450mm × 155mm,With two mobile division plates, can set the division space flexibly. -
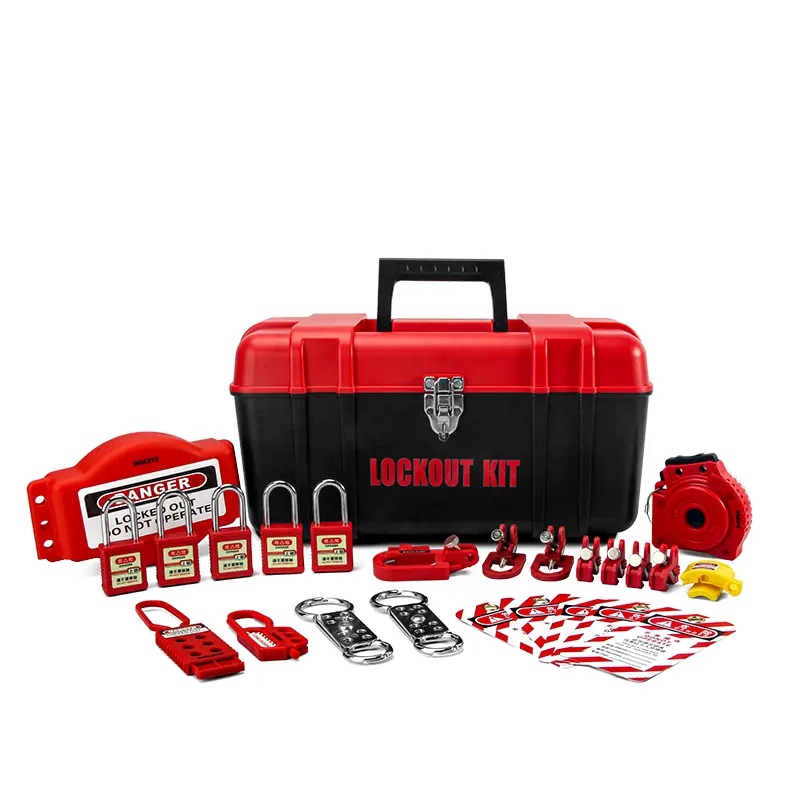

Lockout tagout kits
Lockout Tagout Kits includes:
Safety padlock *1 set
1 set of lockout box
1 set of miniature circuit breaker lockout
1 set of clamp breaker lockout
1 set of 6 holes lockout hasp
1 pcs Aluminum lockout hasp,plug lockout
1 set of emergency stop lockout
Safety Tag
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
-
What Are Cable Lockouts and Why Are They Critical for Safety?
-Cable lockouts are specialized safety devices designed to secure electrical cables, power cords, or data cables during maintenance, repair, or installation, preventing accidental energization, disconnection, or tampering. These devices physically lock cables in place—either by securing plugs in outlets, blocking access to connectors, or immobilizing cable pathways—to eliminate risks like electric shock, equipment damage, or data loss. Cable lockouts are essential for compliance with OSHA (29 CFR 1910.147) lockout/tagout (LOTO) standards and NFPA 70E electrical safety guidelines, ensuring workers and equipment are protected from hazardous energy exposure in industrial, commercial, and residential settings.
-
What Key Standards Govern Cable Lockout Use?
+Cable lockouts must adhere to these primary regulatory frameworks:
1:OSHA LOTO Standard (1910.147): Requires controlling hazardous energy sources, including electrical cables, during servicing. Mandates written procedures, employee training, and proper use of lockout devices to prevent unauthorized cable activation.
2:NFPA 70E (Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace): Specifies lockout requirements for de-energizing electrical systems, including cables, to avoid shock or arc flash hazards.
3:IEC 60364 (Electrical Installations of Buildings): Provides international guidelines for cable safety, including isolation and locking during maintenance. Compliance ensures legal adherence and mitigates risks of non-compliance penalties or accidents. -
How Do You Properly Implement a Cable Lockout Procedure?
+Follow these steps for effective cable lockout:
1:Identify Hazards: Determine the type of cable (power, data, communication) and associated risks (voltage, data sensitivity, motion).
2:Power Down: De-energize the system using proper shutdown protocols, then disconnect the cable from its power source or device.
3:Apply Lockout Device: Secure the cable with a compatible lockout, such as a plug lockout (prevents reinsertion into an outlet), cable tie lockout (immobilizes connectors), or cabinet lockout (secures cable access panels).
4:Tag and Label: Attach a warning tag (e.g., "Do Not Connect—Lockout in Place") with the worker’s name and date.
5:Verify Isolation: Test for zero voltage (if applicable) and ensure the cable cannot be reconnected or manipulated without removing the lock.
6:Release Safely: Remove the lockout only after work is complete, all tools are cleared, and the system is ready for re-energization. Document each step for audit trails and training. -
What Types of Cable Lockout Devices Are Available?
+Cable lockouts vary by application and cable type:
1:Plug Lockouts: Fit over electrical plugs or outlets to prevent insertion/removal, ideal for extension cords, machinery power cables, or portable tools.
2:Connector Lockouts: Secure data connectors (e.g., Ethernet, USB, HDMI) to prevent accidental disconnection during server maintenance or industrial automation work.
3:Cable Tie Lockouts: Use heavy-duty, lockable ties to immobilize cables or secure connectors, suitable for temporary or mobile setups.
4:Cable Management Lockouts: Secure entire cable trays, raceways, or cabinets to prevent unauthorized access in data centers or control panels.
5:Universal Cable Lockouts: Adjustable devices compatible with multiple plug/connector sizes, offering versatility for mixed-cable environments. Choose devices rated for the cable’s voltage, current, and environmental conditions (e.g., waterproof for outdoor use). -
How Often Should Cable Lockout Devices Be Inspected?
+Regular inspections ensure reliability:
1:Pre-Use Checks: Visually inspect locks for cracks, frayed cables, or damaged latches before each use. Test locking mechanisms for smooth operation.
2:Monthly Maintenance: Clean devices and lubricate moving parts (if applicable). Check for wear on plastic components exposed to UV or chemicals.
3:Annual Compliance Checks: Verify against manufacturer standards and regulatory requirements. Replace devices showing signs of degradation (e.g., brittle plastic, corroded metal). OSHA requires lockout equipment to be "substantially durable" and maintained in safe working order. -
What’s the Difference Between Cable Lockout and Tagout?
+While both are LOTO tools:
1:Lockout: Physically prevents cable connection/operation via mechanical locks; only the authorized worker can remove the lock.
2:Tagout: Uses warning tags (e.g., "Do Not Energize") when locking isn’t feasible (e.g., non-removable plugs). Tags rely on human compliance and are less secure than physical locks.OSHA prioritizes lockout over tagout for cables, as locks provide a stronger barrier against accidental energization. Tagout is permitted only when locks are technically impossible, but requires additional safeguards like supervisor approval and double-tagging. -
How to Ensure Cable Lockout Compliance During Audits?
+Prepare your facility with these steps:
1:Document Procedures: Create detailed lockout protocols for each cable type/situation, including diagrams of energy sources and step-by-step instructions.
2:Training Records: Maintain records of employee training on cable lockout use, including initial sessions and refresher courses (required every 3 years per OSHA).
3:Inventory Management: Keep a log of all lockout devices, noting their location, certification dates, and maintenance history.
4:Mock Audits: Regularly review processes for gaps, such as missing locks on temporary cables or unlabeled connectors.
5:Compliance Kits: Use standardized kits with labeled lockouts for quick access during audits, demonstrating readiness and organization. -
What Features Should You Look for in a Cable Lockout Supplier?
+Choose suppliers that offer:
1:Certifications: Products compliant with OSHA, NFPA, and IEC standards, backed by third-party testing.
2:Product Range: Solutions for power cables, data lines, and specialty connectors (e.g., aviation plugs, industrial connectors).
3:Durability: Materials like stainless steel, nylon, or UV-resistant plastic to withstand harsh environments (e.g., factories, construction sites).
4:Ease of Use: Tools-free installation/removal for efficient workflow, without compromising security.
5:Custom Solutions: Tailored lockouts for unique cable configurations or proprietary connectors, ensuring a perfect fit.Reliable suppliers also provide technical support, installation guides, and compliance documentation to streamline your safety program. -
Can Cable Lockouts Be Used for Temporary or Portable Equipment?
+Yes—cable lockouts are ideal for temporary setups:
1:Construction Sites: Secure power tools’ cables to prevent accidental startup during repairs.
2:Event Venues: Lock data cables to prevent disconnection during AV system maintenance.
3:Manufacturing Plants: Use on portable machinery cables to isolate equipment during relocation or servicing.For temporary use, ensure lockouts are visible, labeled, and removed immediately after work ends. Always prioritize locking over tagging for portable devices, as they’re more prone to accidental interference. -
What Risks Come with Skipping Cable Lockouts?
+Neglecting cable lockouts can lead to:
1:Electrical Accidents: Shock, burns, or fatalities from unexpected cable energization.
2:Data Loss/Downtime: Accidental disconnection of network cables causing server outages or corrupted data.
3:Equipment Damage: Forced reconnection of locked cables can damage connectors, leading to costly repairs.
4:Regulatory Fines: OSHA can fine up to $13,653 per serious violation, plus reputational damage from safety incidents.Proactive cable lockout use protects workers, preserves equipment integrity, and ensures uninterrupted operations.